Technology lessons for educational technology integration in the classroom. Content for teachers and students.
Prepare images for Scratch code projects
This lesson covers a process for preparing graphics and images for use with the Scratch coding environment.
Scratch is limited to a specific resolution for images. This resolution I’m sure dates back to the early days of Scratch and the limitations of technology at the time. The resolution for all projects is set to 480 by 360 pixels or less. This is a low resolution compared to today’s standards.
This lesson covers a process for preparing graphics and images for use with the Scratch coding environment.
Scratch is an excellent coding tool developed and maintained by MIT. The goal of the project is to teach young children to code through storytelling.
Scratch includes some images to develop basic stories. The images include backgrounds and Sprites. Sprites are the interactive characters on the stage. The stage is usually represented with a background or Backdrop.
We have the option to include our images for backgrounds and Sprites.
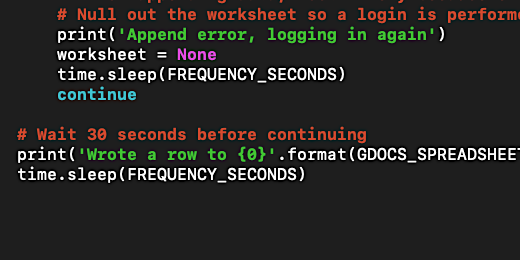
Here is the reason for this lesson. Scratch is limited to a specific resolution for images. This resolution I’m sure dates back to the early days of Scratch and the limitations of technology at the time. The resolution for all projects is set to 480 by 360 pixels or less. This is a low resolution compared to today’s standards.
The Scratch Forum provides information about the image format and resolution. It doesn’t appear they are going to change the resolution any time soon. We can work with this resolution but we need to consider the images used in our product.
Scratch recommends using the PNG, Portable Network Graphic, image format. Another standard recommended is the SVG, Scalable Vector Graphics, image format. We can also use the standard JPEG image format. This is used by all digital cameras and smartphones.
Image formats
Bitmap images
The PNG and JPEG image format is a standard for images known as bitmaps. The images are made of fixed pixels. Each pixel is represented by values that represent the colors for that image part of the image.
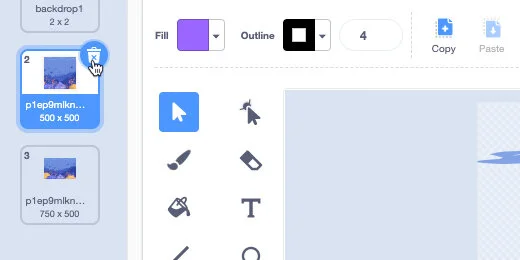
Pixels are not a problem when we are using images with millions of pixels. They become a problem when they are 480 by 360. The image below shows an image at 480 by 360 pixels. The black border is part of my image capture process. Click the image to have it pop out into full 480 by 360 resolution. Looks fine.
The image below is of the same image but enlarged. I took a snapshot of the center part of the original image. The image isn’t as crisp.
The pixels in the image are set at 480 by 360. Enlarging the image is like looking at the image under a microscope. We see all the ugly details. Enlarging the image causes the image to look worse.
Vector images
The other format for use in Scratch is SVG. This image format uses math to represent images. The shapes of the images are not locked in by the size of the image. The image format is often referred to as Vector graphics. The images are lines that can be resized and reshaped without looking quality.
The SVG format is one of many formats. The standard formats used today include EPS, Encapsulated PostScript, and AI. The AI format is from Adobe’s Adobe Illustrator program. Other less common formats include EMF—Enhanced MetaFile and WMF—Windows MetaFile. These formats are typically used on Windows computers.
The image below is an SVG image at 480 by 360.
This is a section of the image at 2,400 by 1,800 pixels. The image quality in vector graphics remains high. This is our goal.
Does it matter?
Scratch is designed for children and storytelling. Children usually aren’t as picky about the images. They look past the low quality in the age of Mine Craft.
Still, I thought this would be one of those teachable moments for those that want to get better quality images in their Scratch products. It provides the opportunity to learn a few more things. A few more technology life skills.
Vector over bitmap
Vector image quality is much better on Scratch than JPG or PNG. Download the lesson images below. There is one image of each JPG, PNG, and SVG. The file downloads as a ZIP file with all the images inside.
Go to the Scratch website, https://scratch.mit.edu. You don’t have to log into an account. This is just for demonstration purposes. Click the Create button.
Close the tutorial if it appears.
Click the Add Sprite icon. Select the option to upload a Sprite from your computer.
Select the JPEG image.
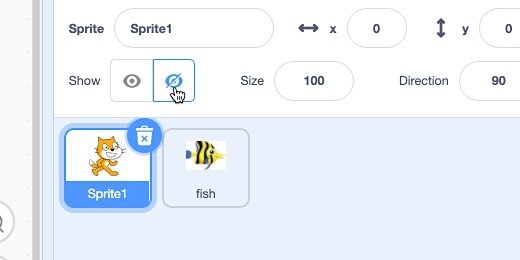
Click the Cat Sprite; click the hide button.
Click the Maximize button.
The JPEG image looks jaggedly and a little blurry. When an image looks like this, it is said to be pixelated.
Click the minimize button.
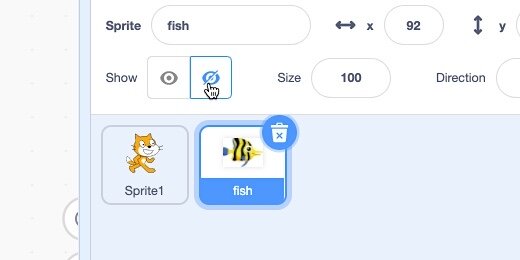
Select the JPEG fish Sprite; click the Hide button.
Upload the PNG version; view the image full screen. The image might be less blurry, but it has jagged edges too.
Minimize the image and hide the PNG image. Upload the SVG version and maximize the image. The quality of this image is much better.
Exit full-screen mode; exit the project.
Vector image resources
There are several places on the Internet to get vector images. There are a couple that I prefer. I prefer these services because they have high-quality images. The image services are free.
More precisely, they are a freemium service. You can download about ten images a day. To download more a day you need to purchase a subscription. I have never needed to download more than 10 images a day.
Using images from these services for free comes with a stipulation. You must give credit to the service or artist in your published product.
The services I like to use are freepik.com and pixabay.com. They offer high-quality images and graphics.
The links below are for the images to be used in this lesson. We are downloading several images to demonstrate how to deal with different formats and image options.
Each link is accompanied by a separate link to the same resource. I don’t have control over the images on these sites. One day they may not be available. The second Lin downloads the same image resource from my Google Drive. You don’t need a Google account to download them.
Large fish download from Freepik
Large fish download from Google Drive
We begin with the first image from freepik.com. This is an image of a large fish. Use the link to see the fish preview and click the Download button.
Click the green Free Download button.
Freepik provides an attribution link for the image. We are not publishing this image for the lesson so there is no need to copy the link at this time.
The image is downloaded to your computer in a compressed ZIP file. Your computer should extract the contents of the file as soon as it is downloaded. If not, you will need to double-click the ZIP file to extract the images and files.
Inside the folder, there are two images and a couple of text files. The text files contain information about the license for the image and attribution.
This image contains two image files. One is a standard JPEG; the other is an EPS file.
The EPS file needs to be converted for use in Scratch. I am not going to use a vector creation program like Adobe Illustrator. I will assume you don’t have one of these tools. I am also assuming your students don’t have access to this program on their computers. They are probably using a Chromebook.
We are using some free online tools. This makes it easier for teachers and students with Chromebooks and those that don’t have vector applications.
All we need to do is convert the file to the SVG format. I have links to three services. Each service is free. The services limit the number of files you can convert. I often bounce between the three services if I need to convert several files. I will cover the process for each service during the lesson.
Cloud Convert: https://cloudconvert.com/
Convertio: https://convertio.co/
Zamzar: https://www.zamzar.com/
Use the Cloud Convert link. Click the Select file button.
Go to the image folder and select the EPS file.
The file is placed into a conversion cue.
Use the convert selector to see the vector image options; select the SVG format.
Click the Convert button.
The file is uploaded and the conversion process begins. The process takes several seconds. I can also take a couple of minutes. It depends on how many conversions the site is working on at any moment.
A preview of the image appears when the conversion is complete. Click the Download button. Place the image inside the image folder downloaded from Freepik.
Scratch fish sandbox
Go over to the Scratch website—https://scratch.mit.edu/. Login and create a new project. Set the title of the project to Fish graphics.
Select the Cat Sprite; click the hide sprite button.
Click the Add Sprite button; choose the upload option.
Go to the image folder and select the SVG file.
The fish is added to our project Sprite library.
Change the name of the Sprite to Drink-Fish.
Select the Costumes tab.
The image is too large. It doesn’t fit inside the Sprite canvas.
Click on any part of the image. Parts of the image are selected separately from the complete image. The illustration is created with several layers of shapes. Each shape can be moved and modified. Don’t move any of the shapes! If you did, click the undo button.
To resize the image, we need to gather all the shapes and place them in a container. We are grouping the shapes into one representation of the illustration.
The graphic tools in Scratch are basic. There is no tool to select everything on the canvas. We need to use our traditional computer shortcut keys. On Windows and Chromebook—press the key combination Control+A. On Mac—press Command+A.
Click the Group button.
Click the Zoom out button to see as much of the fish as possible.
Move the image down and to the right. Stop when you see the top left corner appear inside the dark gray checkerboard.
Use the corner handles to resize the image. Using the corner handles keeps the image aspect ratio and avoids distorting the image.
Scratch places a center reference marker on the image. Use the marker to align it to the center of the Sprite canvas. The center of the Sprite canvas has a dark dray marker.
Place image marker atop the canvas marker.
This Sprite is crisp and looks nice.
Multiple images
The first image was easy. Not all the images we want for a project are this easy. Let’s take a look at one with multiple images.
I like illustrations with multiple images. I get several images for a project from one illustration download.
Use the link below to download another illustration from Freepik. Click the Download button and open the ZIP file to reveal the folder with the images.
Sea animals download from Freepik
Sea animals download from Google Drive
This file contains an illustration with several fish images.
Select the EPS file.
Select the SVG option from the vector section.
Click the Convert button.
Click the Download button when the conversion is complete.
Place the converted image in the folder with the other images. Return to the Scratch project and upload the image as a Sprite.
Click on the Drink Fish Sprite and hide it.
Click on the Sprite we uploaded and select the Costumes tab.
Not all the fish illustrations fit within the canvas. They are all there but we can’t see them because they are spread out over a wide area.
Use the keyboard combinations to select everything in the canvas area. The keys are Control+A on Windows and Chromebook; Command+A on Mac.
We see the outlines of the other fish illustrations.
Click the Group button.
This illustration is much larger than the first example. You need to gradually move the grouped shapes down and to the right until the bounding corner appears.
You need to grab the illustrations to move the group. An empty area will not move the illustration.
Use the corner resize handle to make the illustration smaller. The illustration is so large you will run out of space.
Drag the illustration up and onto the canvas to finish resizing.
Make sure you can see all the images.
Keep the illustration selected; click the Ungroup button.
Click away from the illustration to deselect the grouped animals. You can also press the ESC key on your keyboard.
Click the Zoom-in button once; scroll to see the first fish in the upper left.
Draw a selection box around the first fish only. Make sure not to include any part of another animal.
Click the Group button; click the Copy button.
Go to the Add sprite button; select the paint option.
Click the Paste button.
Move the fish to the center of the canvas. Use the center reference mark to center the image.
Use the resize handles to make the illustration larger. Make sure it fills most of the canvas. The canvas is light gray area in the center.
Click on the Sprite with the collection of sea animals.
Go to the Costumes section; draw a selection around the crab illustration.
Group the illustration.
Click the Copy button.
Create a new Sprite with the Paint option.
Paste the illustration.
Center and resize it on the canvas.
Repeat this process with all the fish illustrations. In the end, you will have nine more fish Sprites.
Use the project link below to see each of the sprites as they should appear in your project.
https://scratch.mit.edu/projects/462185532
Hide the Sprites for the next part of the lesson.
Backgrounds
The process is much the same for background images. Use the link below to download the next image from Freepik.com.
Underwater background download from Freepik
Underwater background download from Google Drive
Download the illustration; unzip the file.
This illustration has four image files. One of the file types is for Adobe Illustrator. The EPS and AI files have two images embedded in the illustration. Artists might do this to conserve on the number of files distributed. The illustrations represent the same image in different sizes or aspect ratios.
We are going to use the Adobe Illustrator file this time. Use the link below to access Zamzar.
Use the Add Files button and select the AI file for upload.
Select SVG from the convert menu. Click the Convert Now button.
Zamzar offers three file download options. The first option will download both illustrations in one file. The other files represent each of the two illustrations. Download the first file to get both.
The illustrations are in a compressed file. Open the compressed files. Place the illustrations inside the folder. Return to the Scratch site. Click the Add Background button and choose Upload.
We are going to upload both files. Select the page 01 file and upload it first. Use the same process to upload the second illustration page.
The backgrounds are added to the Backdrops section. The tab opens after the image is uploaded.
Click on the first backdrop we uploaded. This illustration is wider than it is tall. Scratch has trouble with illustrations that are not in the 4:3—four-by-three aspect ratio.
Select the second illustration. This one is closer to the 4:3 ratio. It looks better than the first.
The first illustration isn’t usable. Select the illustration and click the Trash icon.
This illustration is like Sprite imports. It is a group of shapes and lines. Select all the shapes by using the shortcut keys; click the Group button.
The area outline with a white border represents the visible stage area. Resize the backdrop so most of it appears within the area.
The background is ready for a nice ocean project.
Regular images
We can’t always find the image we want as an illustration. Sometimes we need to use a regular image. We will lose some detail when using regular images. There is a way to minimize the pixelation or detail loss.
We are going to use Google Drawings to resize and crop the image before importing. Scratch prefers background images in the 4:3 aspect ratio. Cropping the image to this size reduces the amount of some pixelation.
Use the link below to download the next image.
Underwater scene download from Freekpik
Underwater scene download from Google Drive
Create a new Google Drawing document. Use the link below to create one.
https://drawings.google.com/new
The Google Drawing canvas is already at the required 4:3 aspect ratio.
Go to the Insert menu option and select Upload from the computer.
Select the image to upload. The image needs to fill the drawing canvas. Use the corner handles to resize the image.
The image is wider than the canvas. The part of the image that is off the canvas will be cut off during export. We need to control what is cut away.
Make sure the image is selected; click the Crop tool.
Black crop handles appear around the image. They are in the same positions as the Resize handles.
My image extends off the canvas on the right side. I need to grab the crop handle and move it toward the left.
A crop line follows the resize handle. Move the handle to the edge of the canvas. Use the ruler as a guide. The line will also snap to the edge of the canvas.
The area that is slightly dimmed will be hidden on export. Part of the Clown fish’s tail will be cut away along with the nice reef. We don’t want this to happen.
Click and drag the image to the left. It’s a little hard to see but the right edge of the image is moving to the left. The red horizontal line is the vertical center alignment guide. Use the guide to keep the image centered vertically.
Moving the image with the mouse in crop mode doesn’t give much feedback when moving. Use the Left or Right keys on your keyboard to move the image left or right.
The arrow keys jump the image about five pixels at a time. You can get finer movement by holding the Shift key while using the left and right arrow keys.
Move the image to the left so the right edge of the image is on the canvas. Press the ESC key to exit Crop mode.
Click File; go to Downloads and select PNG image.
Switch over to Scratch and upload this image as a Backdrop.
Transparent backgrounds
I’m not talking about images that are transparent. I’m talking about images of an object without a background.
When creating projects we might need an image of an object or person without the surrounding background. The image below is an example. The gray and white squares around the turtle represent the transparent part of the image.
The latest online technologies and services make the process of removing backgrounds from objects simple.
Use the link below to download the next image.
Underwater turtle download from Freekpik
Underwater turtle download from Google Drive
The image is of a Sea Turtle. It is the only object in the image. There is a lot of contrast between the turtle and the background. This is key to getting good results.
There are a couple of sites I use to remove backgrounds from images. The links are available below.
Use the link to access https://remove.bg. Click the Upload image button; select the image.
The process begins almost immediately. The original and processed images are shown side by side.
Use the crop handles to crop away unwanted empty background.
Click the Download button. Click the Download in Low-Resolution button.
Upload this image to the Scratch project as a Sprite. The turtle is over the backdrop and looks like it is part of the underwater scene.
Student images
We want our students to be part of the storytelling project. Adding students to a project is just as easy. Use the link below to download an image of this student with a graduation cap.
Open another tab and go to https://remove.bg; upload the image. Download the image and add it to your project as a Sprite.
Use the link below to see how I combined the image with a backdrop.
https://scratch.mit.edu/projects/465066313
One more example
We don’t need to download images from a web service. We have nice high-quality cameras on our phones. Use the camera to take pictures of students or props to use in the story.
Our cameras take good high-resolution images. These images are often too large for the online background remover to process. The limit for https://remove.bg is 12MB.
Here is a freemium online tool that will help us reprocess the image. Reprocessing the image will reduce the file size without reducing quality. While we are on the site we will crop the image to focus our attention on the student.
Use the link below to download the next image.
The file size for this image is over 13MB.
Open a tab and go to https://befunky.com. This is a freemium online photo editor. The free services are all we need for this example.
On the site, you can log in with a Google, Facebook, or email account. We don’t need to login for this example. I encourage you to create an account and login. This will save your work.
Click the Create button. Click the Get Started button if you didn’t create an account or log in.
Select the Photo editor option.
Click the Open option and select open from the computer.
Select the image we just downloaded. The image opens in an editor. We don’t need to do anything special. All we do is save the image. Click Save and select Computer.
The estimated size for the image is now 1.6 MB. Don’t download the image yet.
Let’s modify the image before we save it. Click the Cancel button.
Click the Crop tool
Use the corner handles of the Crop box to cut away a lot of the background.
Crop the image so the focus is on the little girl.
Click the Check button to apply the crop.
Click the Save button and save the image to your computer.
Go to the background removal website—https://remove.bg. Upload the image and remove the background. Download the image and add it to your project as a Sprite.
Use the link below to see this image used with a backdrop. The backdrop is another image from Freepik.com.
While Loop on mBot
In this lesson, you will learn how to use a loop to accelerate and decelerate. Loops are an important part of developing autonomous programs. The purpose of a robot is to perform a series of tasks. Most tasks are specific to a particular objective. Many tasks include repetitive operations. Robots can perform repetitive tasks all day long.
In this lesson, you will learn how to use a loop to accelerate and decelerate. Loops are an important part of developing autonomous programs. The purpose of a robot is to perform a series of tasks. Most tasks are specific to a particular objective. Many tasks include repetitive operations. Robots can perform repetitive tasks all day long.
This lesson will cover a simple task. The robot will gradually accelerate to its top speed; it will then reduce speed to a full stop.
We will be using the remote to start and control the process.
The link to the finished code is available below.
https://planet.mblock.cc/project/502092
We are building the program with the basic building blocks that are particular to this task. The aim is to show you how programmers develop programs. Programmers build and test parts of the program as they go. The program evolves to become the completed product. Testing is important during the development process.
The online version of the mBlock coding environment is at https://ide.mblock.cc
Building the program
Open the mBlock application. Click inside the project name field and set the name to accelerate-decelerate. Click the Save button.
Go to the Devices section and click the Add button.
Select the mBot library; click the OK button.
We can set the mBot library to be loaded each time we create a new project. Click the Star icon. The mBot library will load each time a new project is created.
Delete other Device libraries. This prevents us from accidentally selecting code blocks that don’t work with the mBot.
We want the robot to move forward and accelerate. The process begins when the Up button on the remote is pressed.
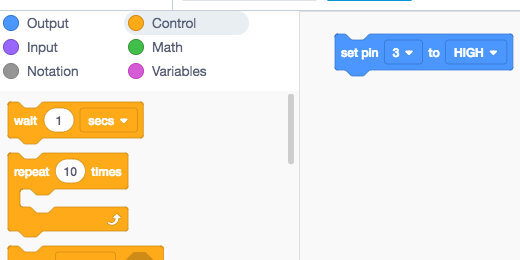
Go to the Control functions section and place an **if…then** code block on the canvas.
Go to the Sensing section and get the **IR remote pressed** code. Place it into the **if…then** parameter.
Choose the **Up** option from the button selector.
We want the robot to slowly accelerate when the Up button is pressed. To perform the acceleration process we need to use a loop. We want the loop to repeat until it reaches the maximum velocity.
We don't know the robot's velocity. We only know the amount of energy applied to the robot motors. The energy is supplied by the batteries. The batteries supply current to the robot's controller and the motors.
The energy we supply to the robot's motors is like the gas pedal on a car. We supply fuel to the engine and the engine, in turn, uses the fuel to propel the car forward. A speedometer in the car lets us know how fast we are going.
The robot does not have a speedometer, so it's like driving a car without a speedometer. We don't know how fast the robot is traveling. We can take some measurements and perform a bit of math to know the robot's acceleration and velocity.
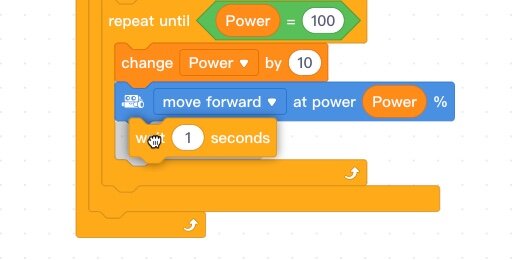
There are three loop options we could use. We are using the repeat **until loop**. We are using this loop because we want the robot to accelerate **until** it receives the maximum amount of energy available.
Go to the Control section. Place a **repeat until** loop within the **if…then** condition.
Go to the Action section. Place the **move forward at power** code block inside the loop.
We need a way to increase the power applied to the motors. The power applied to the motors is based on a percentage of the available battery power. The current value in the move forward code is constant. It doesn't change while the program is running. To update the percentage, we need a variable.
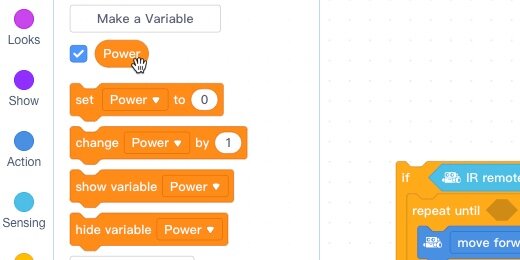
Go to the Variables section; click the **Make a Variable** button.
Use **Power** for the variable name. Select the option to use this variable for this sprite only. Click the OK button.
Grab the Power variable.
Place the variable into the Power parameter.
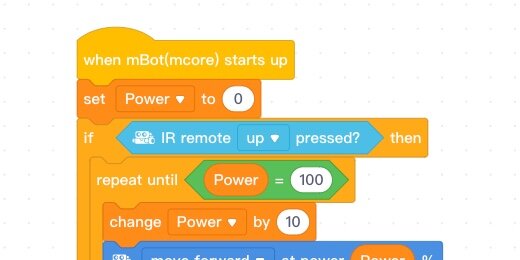
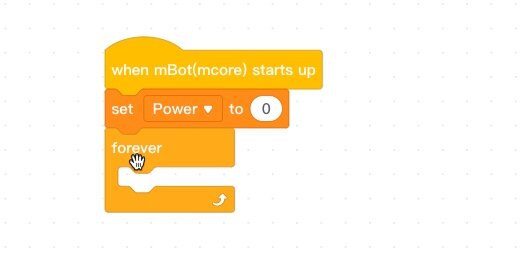
The variable accepts input from several sources. Attach the **set Power** code to the beginning; before the **if…then** code.
It is recommended to initialize variables before they are used. This block is not in the loop because it sets the initial value of the power before it is changed. The initial value is set to zero.
Place the Change Power code inside the loop and above the Move forward code. This code, increases, the value of the power applied to the motors. The value for the power ranges from 0 to 100 percent. The power can be increased by any increment we want. The increment determines the rate of acceleration. Small increments result in slow acceleration. Large increments result in a fast acceleration.
Let’s begin with an increment of 10 percent. Place 10 inside the parameter.
This will repeat until the robot reaches a maximum of 100 percent. The loop needs a condition. The condition informs the loop when it is time to stop looping.
Go to the Operators section. Look for the **Equal to** operator. This is an evaluation operator. It evaluates if something is equal to something else. This isn't like the equal sign in traditional math. This sign looks to see if two or more values are the same.
Place the evaluation operator inside the repeat parameter.
Go to the Variables section. Place the Power variable inside the left side of the evaluation.
Change the value from 50 to 100.
This is a good place to stop and test what we have done. The robot is going to be moving, so we need to make sure it stops at the end of the loop. Go to the Actions section; place the Stop moving code at the end of the if..then code.
Connect the robot to the computer and turn the robot On. Click the Connect button. Select the port for your robot and complete the connection.
Click the Upload button.
Go to the Events section. Attach the When mBot starts up code to the beginning.
Click the Upload button.
Disconnect the robot and place it on the ground. Please, don’t do this on a table or desk.
Press the Up arrow on the remote.
**Nothing is happening!**
Sorry, I set this up as our first bug in the code. I often make this mistake.
It also provides a teachable moment.
Code that is waiting for input from a user needs to be placed in a Loop. This forces the code to keep checking for input.
Connect the robot back to your computer. Detach the if…then code from the set power code.
Get the Forever loop from the Control section and attach it below the Set Power code.
Take the If…Then combined code blocks and place them within the Forever loop.
We can upload this code to the robot and the robot will receive the command from the remote. The robot will power up and move forward. You will see it move away at the fastest speed. It won’t perform a gradual acceleration. This introduces another bug.
The controller processes the instructions very fast. The processor on the controller is not as fast as the one on your typical computer. It is still fast. It processes information at 16 MHz. That is 16 Mega-Hertz or 16 million instructions per second!
The processor increases the speed so fast that it reaches 100 percent almost instantly. We need to slow things down.
Go to the Control section and place a Wait 1-second delay after the Move forward code. With the code, the robot will move forward at a certain Power for One Second. The Power will increase to the next level and the robot will move at that Power level for One Second. It will repeat this process until the power level reaches 100 percent.
The robot is set to accelerate until it reaches 100 percent of the available power. It will keep going unless we do something to slow it down or stop it. Give it a try. No bugs this time.
Not on the table or desk!
Let’s slow the robot and bring it back to a stop after accelerating. The next process is to decelerate the robot. The code to do this is almost identical to the code for acceleration.
Move your mouse pointer over the Repeat until code. Right-click on the code; select duplicate.
The duplicate code attaches itself to the mouse pointer. Move the pointer to the end of the **Repeat until** code. Wait for the code blocks to separate; release the code. The code must be right after the first repeat until code.
The second code will repeat the loop until the Power level is zero. Place the number 0 into the comparison operator for Power.
We need to decrease the power supplied to the robot through each cycle. Change the positive 10 increments with negative 10, -10.
That is all we need to do. The robot will accelerate up until it reaches 100 percent of the available power. It will then begin to decelerate until no more power is sent to the motors.
Some lights
I like to add some visuals to my robot code. It provides feedback, so I can see at what stage of the code the robot is operating.
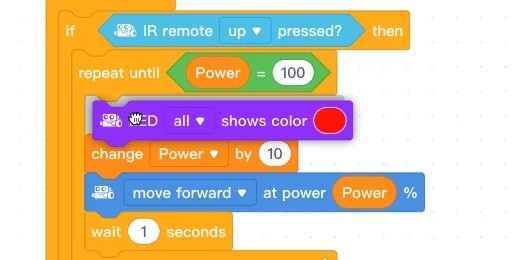
Go to the Show section. Get the **LED all** code. Attach it to the first repeat until loop at the beginning.
Click the color selector and move the color slider; choose green. When the LEDs are green, I know the robot is in the acceleration loop.
Add an LED code block to the second repeat loop. Place it in the same position. Leave the color set to red. When the LEDs are red, I know the robot is in the deceleration loop.
Place one last LED code block outside the second repeat loop. Select the color picker; move the brightness slider to the left. This turns the LEDs off.
Upload the code to the robot. Place the robot on the floor and press the Up arrow on the remote.
The program is in a loop. Press the Up arrow when the robot stops to repeat the process.
Electric circuits and Arduino with TinkerCAD
In the lesson, we create a basic circuit in TinkerCAD. We create a basic LED circuit. We combine the basic circuit with an Arduino microcontroller. We use the microcontroller to turn the LED ON and OFF. We take it one step further and program the LED to blink. A good lesson to learn the fundamentals.
Coding Circuits With Arduino in Tinkercad
An Arduino is a microcontroller. A microcontroller is a very simple computer that accepts basic code. It translates that code into instructions that interact with the physical world. In this lesson, we will use a microcontroller to act as a switch.
Click the link below to see the completed project.
https://www.tinkercad.com/things/3sufhjgf15T
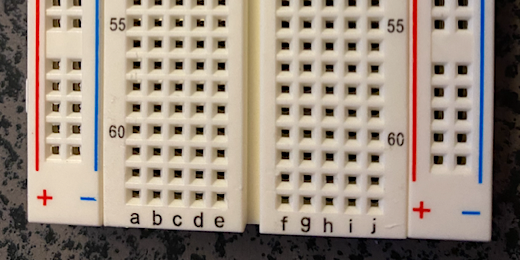
Create a new circuit in TinkerCAD. Add a Breadboard to the work area. Place one LED on the Breadboard and place two jump wires. Connect one jumper wire to the positive rail. Connect the other to the negative rail. Make sure to connect the anode to the positive lead and the cathode to the negative lead. The Anode on the LED is the the one with the bent wire.
LED on breadboard
Click on the Components button and find the Arduino Uno R3 microcontroller.
Arduino Uno R3 component
Place the microcontroller to the left of the Breadboard. Several components are part of the Arduino board. Let’s look at a couple of these components.
Arduino alongside the breadboard and led circuit.
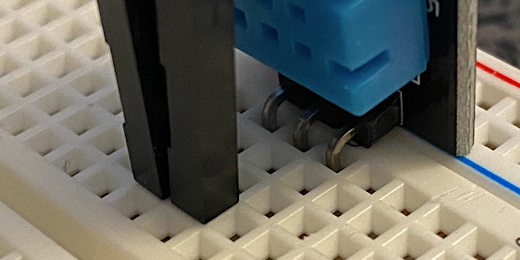
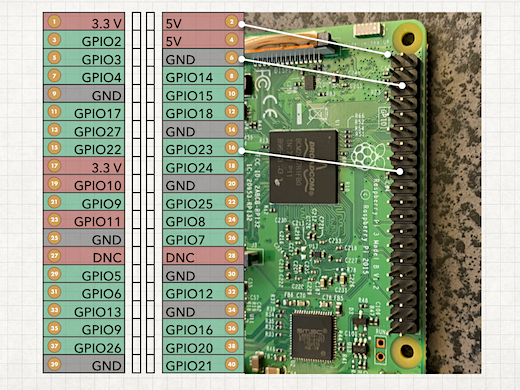
The holes along both sides of the board are GPIO pins. This stands for General Purpose Input/Output pins. Each is a connector that links to our Breadboard with a jumper wire. Most of these are with a number. These numbers identify the pins in our code. The code we develop on the board can reference these pins as either input or output. There is one connector labeled GND. This is the ground connector or the negative terminal in our circuit. The Arduino provides coded instructions to the components on the board. It also provides the necessary current to make the components work. The GND is the same as the negative terminal on a battery. The other connectors marked with a number are the same as the positive terminal on a battery.
A physical Arduino board connects to a five-volt power supply from a computer USB port. The Arduino itself supplies the same 5 volts to components. For some components, this is too many volts. In our example, the 5 volts will destroy the LED on the Breadboard. We will be adding a resistor to limit the amount of current going to the LED.
GPIO PINs on Arduino
Connect a jumper wire from the GND connector on the Arduino to the negative rail on the breadboard. Take another jumper wire and connect it from the number 3 GPIO to the positive column. I moved the board so you could see the connections. I also color-coded the wires.
Jumper wires from breadboard to Arduino.
This isn’t enough to turn on the LED. We need to do a few more things. Click on the Code Editor button.
Code editor button
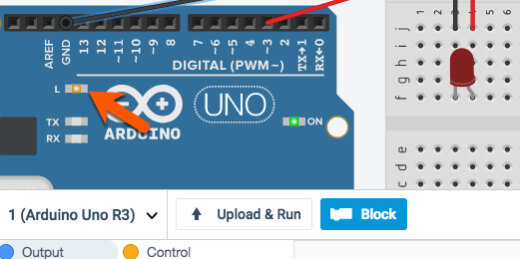
A coding panel will open at the bottom of the page. We use blocks to develop code. Like the blocks used in Code.org or Scratch. There is already a program in the editor. This is the standard code included each time we place an Arduino board onto the workspace. This code instructs the LED on the Arduino board to blink. This is not the LED on our Breadboard. The Arduino has a small LED on the board. Click the Start Simulation button to see the LED on the board blink.
LED code block for Arduino.
The blinking LED is on the left side of the Arduino logo. Stop the simulation.
Blinking LED on Arduino board.
We don’t need this code. We want to control the LED on the Breadboard. Click on the first code block and drag it to the trash can icon. This takes everything that is connected to it.
Removing the standard LED code.
We need a little more room to code. Move your mouse pointer to the top edge of the coding panel until you see the arrow change. Click and drag up to expand the coding panel.
Widen the code area.
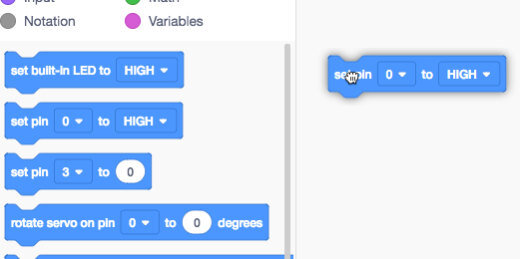
The coding panel has different sections of code. We will be using code blocks in the Output section. Drag the set pin code onto the coding canvas.
Set pin code block onto canvas.
Most code blocks have options. This code block includes a PIN and a state. The PIN references the connector we used to send current to on the Breadboard. This is the positive jumper wire we connected earlier. We connected the wire to pin 3. The options in the code block are arguments.
The term argument comes from mathematics. The argument of a function is a specific input to the function. It is an independent variable like the pin in our code block. This code block has two arguments.
Set pin code and parameters.
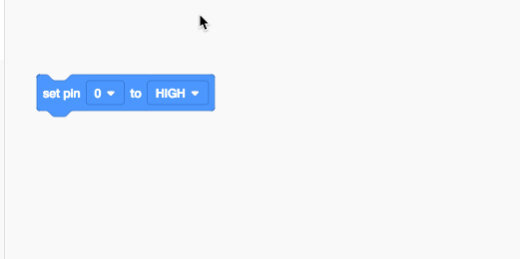
Change the pin to 3. The second argument has two states. A state has one of two options. A state can be on or off. The state is set to high. A high state is the same as ON. The other option is a LOW state. This is the same as OFF. Computers read everything as either ON or OFF.
That’s all we need to get started. Click the Start Simulation button. Resize the code block panel to see the LED.
Parameter set to pin 3.
The LED will change color to show that it is on. There is an exclamation mark next to the LED. This exclamation mark is a warning. The current going through the LED is too high. In the simulation, we get a warning. In a physical board with a real LED the LED would burn out and won’t work again. This is why testing or prototyping is useful. LEDs aren’t expensive but expensive enough that you don’t want to be burning them out all the time.
To avoid burning out LEDs we need to use resistors. Resistors restrict the flow of current to components. Every circuit includes voltage, resistance, and current. Current is the part of the equation that does all the work. Think of electric Current like water flowing through a river or stream. Resistance is the width of the river or stream. Narrow streams have more resistance than wide streams.
LED light with warning.
Stop the simulation and close the code editor. We need to make room for the resistor. Move the LED to the other side of the board. Place it in column A.
Changed position of LED on breadboard.
Open the components panel and find the resistor.
Resistor in component panel.
Place the resistor so it bridges the gap between the two halves of the board. Make sure the resistor is in the same row as the anode and the positive jumper wire.
Resistor on breadboard.
The row connections do not span across the board between E and F. Add a jumper wire to complete the circuit.
Jumper wire to complete circuit.
Run the simulation and the LED should light.
Blinking LED
The code we used in the previous example turned the Arduino into a glorified switch. We can do so much more with Arduino.
Click the code editor button to open the coding panel. Click the Control code block category and look for the wait code block.
Wait code block.
Place the wait code block below the set pin code block. The wait argument is set to one second. Leave the argument at this value. Go back to the Output code block category. Place another set pin code block onto the canvas below the wait code block.
Second set pin code below wait block.
Set the pin value to 3 and the state to low. Run the simulation. The LED will turn ON and OFF. The OFF state is too short. Arduino is a very simple computer but it is still very fast. It processes our instructions in fractions of a second. We need to instruct the code to slow things down so we have time to see the changes.
Set pin block with updated parameters
Go to the scripts panel and find a wait code block. Add a wait code block after the last pin code blocks. Leave the wait value at one. Run the simulation again. The LED will turn on and off over and over again. The code we write does not include a loop function but the Arduino repeats the code anyway.
Second wait code block
The code blocks we use are representations of written code. The written code is on the right side. The code has two main sections or functions. The void setup function sets pin 3 as the output pin for the instructions.
The void loop function is where we write the main part of our code. The void loop repeats the code until the simulation stops. On a physical Arduino, we need to turn the power OFF.
The script represented from the code blocks
The void loop instructs the board to set the power to pin 3 to high or On then wait one second. After one second the power to pin 3 is set to low or turned off and then wait one second. The instructions repeat all over again until we stop it by removing power from the Arduino board.
Weather Station Project: Lesson 9
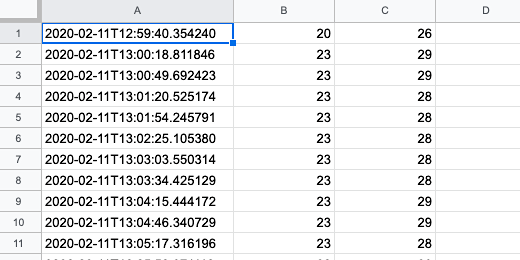
This lesson creates and formats charts with the temperature and humidity information. The charts will display the current day’s temperature and humidity. To do this we will filter our query for sensor readings gathered today.
Line charts
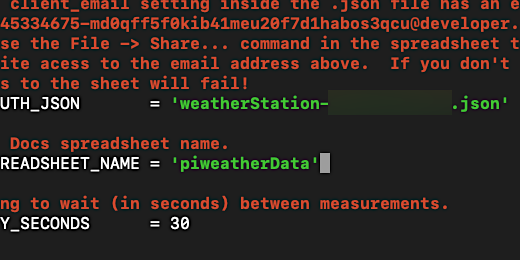
Line charts are used to represent trends in data over time. That describes the information we are collecting. The sensor takes temperature and humidity information at set intervals. That interval is currently every thirty seconds.
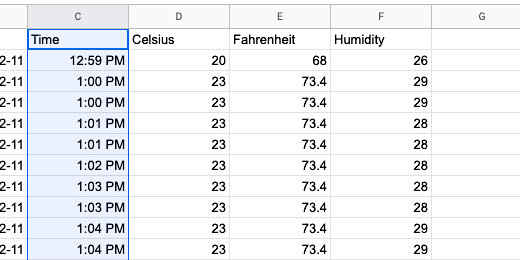
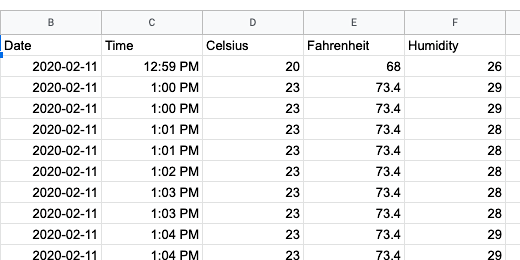
We need to select two columns of data. The first will be the time. The second will be the temperature in celsius. We will create charts for Fahrenheit and humidity later.
We don't need to represent all the readings in our chart. For this chart, we will take the first 24 readings. Click on the time heading and drag the mouse down the column to row 25.
Move the mouse over to the adjacent column and select the corresponding celsius data.
Click Insert on the menu. Go down the list of options and select Chart.
Google will attempt to select a chart type for us. In my example, it chose a bar chart.
A panel opens to the right of the spreadsheet. This panel is used to edit and configure chart settings. Click the Chart type selector. Choose the first line chart option.
The chart isn’t much to look at now. This will change when we modify the sensor reading interval. The temperature readings are on the left.
The chart shows a blue line at the bottom. This represents the time intervals. Go to the panel. Click Use column C as labels.
The time intervals appear on the x-axis.
Click the Customize tab in the Chart editor panel.
Click the chevron next to Chart & axis titles.
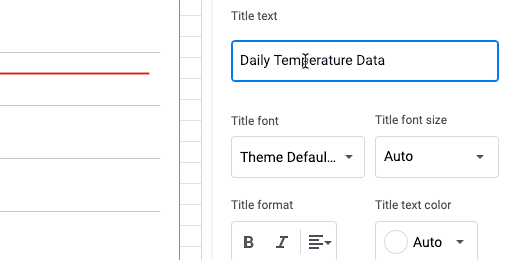
Title the chart, Daily Temperature Data.
The title appears at the top left on the chart.
Click the text alignment selector and choose center-align.
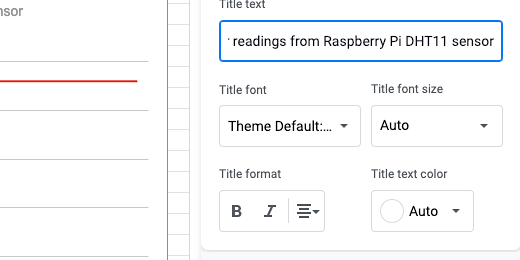
Click the title selector and choose Chart subtitle.
The subtitle is Sensor Readings from Raspberry Pi DHT11 sensor. Change the text alignment to center.
Go to the title selector and choose the Horizontal axis title.
Set the title to Time. Align the text to the left.
Select the Vertical axis title option.
Set the title to celsius.
Click the chevron again to collapse the section.
The tile labels don’t show every time reading. It would be convenient to have all the readings. Open the horizontal axis section.
Click the option to treat the labels as text. The labels are fitted within the horizontal axis.
The data in the chart is from the first day when we began accepting readings. New readings are appended to the end. Today’s sensor readings are at the bottom of the sheet. We need to filter and sort the sensor data.
Today’s Temperature
To display the temperature for the current day we need to filter the data. We do this within the query function.
We are going to create a new sheet for this chart. Click the Plus button to create a new sheet.
Double click the sheet name and change the name to Today’s Temp.
Inside of Cell A1, we will query the data. We only need the time and temperature information.
Type =query(‘sensor data’!B1:E,”select *”,1)
The name of the sensor data sheet is in single quotes. This is necessary because there is a space in the sheet name. The data range begins on cell B1. This is where we have the date information. The data in column E contains the temperature information in Fahrenheit. Using the column notation without a number after E selects every cell in columns B,C,D and E. Replace -1 with 1.
To get the readings from today, we need to modify the query. Click on cell A1. We are going to use the Formula Bar to edit the query. Place the cursor after the asterisk.
Add this parameter to the query after the asterisk.
Where B = date ‘“&text(today(),”yyyy-mm-dd”)&”’
This parameter instructs the query to use today’s date as the filter. The filter looks in column B. If there is data for today’s date, then it is listed.
It may look like there are three single quotes after date. It is a single quote followed by a double quote. The order is reversed after the ampersand.
There is a lot of new stuff going on here so I’ll go through the parameters. We are instructing the query to select everything in the columns where the contents of column B match today’s date.
The single quote and quotation marks are like parentheses. The single quotes surround quotation marks and the parameters. The date for today is represented as text in the form of year, month, and date.
Today’s Temperature Chart
We spent some time customizing the chart earlier. We will use this same chart for our new sheet. Go back to the sensor data sheet. Click once on the chart. Click the three dots in the upper right corner. This is called the action menu. Select the option to copy the chart.
Go back to Today's Temp sheet. Click Edit and select paste.
Click the chart action menu and select the Edit chart option.
Click in the Data range field. Erase the data range.
Replace the range with B2:C25.
This chart represents the temperature in celsius. We will use another chart to represent the Fahrenheit temperature information.
Make a copy of the current chart. Click the actions menu and select Copy chart. Click edit in the Google Sheets menu and select paste.
Click the actions menu on the duplicate chart and select Edit Chart.
Erase the data range. The data for this chart spans two separate columns. Those columns are not next to each other. We need to select the columns separately. Type B2:B25,D2:D25. Note that the selections are separated by a comma.
Go to the Customize section of the Chart editor. Open Chart & axis titles. Select the Vertical axis title. Change the title from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
The titles are looking a little bland. This makes it difficult to distinguish. Change the chart color to help identify the charts. Go to the Chart style. Click the background color selector. Choose a light color for the background. A light color will help keep the text on the chart legible.
Repeat the process with the chart with the celsius information.
Humidity Chart
The chart to report the humidity information is similar to the temperature chart. Click the Plus button to create a new sheet. Rename the chart to Today’s Humidity.
Let's take a look at the sensor datasheet. The humidity data is in column F. We will query the data from columns B, C, and F.
Go back to the Humidity sheet and enter this query.
=query(‘sensor data’!B1:F,”select B,C,F”,1)
The select parameter is used to choose the columns of data to display.
We are going to filter the data so only the current day’s humidity information is displayed. We will use the same parameter used for Today’s temperature reading.
Use the Formula bar and place the cursor right after the letter F. Add this parameter.
Where B = date ‘“&text(today(),”yyyy-mm-dd”)&”’
Today’s Humidity Chart
Go to Today's Temp sheet. Choose one of the charts. Click the actions menu and select Copy chart. Return to Today's Humidity sheet and paste the chart. Click the chart action menu and select Edit chart. Erase the current data range. Replace it with B1:C.
Go to the Customize tab in the chart editor. Open the Chart & axis titles. Select the Vertical axis title. Change the title to Percentage.
Select the Chart title. Change the title to Today’s Humidity.
Open the Chart style section. Change the background color.
Weather Station Project: Lesson 8
In this lesson, we explore automation with Google Apps Script. The automation is helpful if we intend to run our weather station project for several weeks. The automation with Google Apps Script will update the formatting of the date information. With automation, we will split the date information and the conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
Formatting with Google Apps Script
Introduction
In the previous lesson, we used the split function to split the date and time information. This function works for all the data up to the last cell in the sheet. The last cell is typically cell 1,000 for new sheets. New date information added beyond this cell doesn't have the function applied. This isn't a problem unless we expect to gather lots of data.
We need to manually copy the function down the new rows if we plan to collect lots of data. That is one way to update the cells. Another way is to do with programmatically. This involves adding a small program to our spreadsheet.
Here is a disclaimer. You don't have to go through this lesson if you plan on having a short run of the weather station. This really all depends on how much data you want to collect. Collecting data every thirty-second is really too much. I would say that collecting sensor information every half-hour to one hour is a little more reasonable.
Collecting data each hour will use up the one-thousand rows in about six weeks. Collecting sensor data every half-hour will fill the rows in half that time. One-thousand rows are therefore good for three to six weeks worth of sensor data. More data requires more rows. Google sheets will automatically add more rows as needed. The split function and temperature conversion are not automatically applied to the corresponding new data.
This happened to me while creating the lessons. I left the code running most of the day and the data went into well over two-thousand rows.
Gathering data from the sensor every 30 seconds is not the best. We will adjust the time interval later. I will keep the code set to 30 seconds for now so we can build the graphing tools.
The formatting needs to be updated as new data is added. To automatically update the function for new rows I want to create an app script. The app script will run at specific intervals.
The script
Google includes a script editor option for most of its applications. The script editor is available in the Tools menu. Open the piweatherData spreadsheet if it isn’t already open. Click Tools and select Script editor.
The code editor opens in a tab to the right of the spreadsheet. The code is created within functions. Google Sheets has one function ready for us to use. App scripts and functions are created in projects. The project is currently untitled.
Click the Untitled project name.
Name the project splitDate.
The function of the project is titled myFunction. Change the function name to splitDateFunction.
The code in Google Apps script is case sensitive. The code needs to be typed with the appropriate upper or lower case characters. Errors in the code are often the result of forgetting to properly format the commands. You can copy and paste the commands from my instructions. As always, I encourage you to type out the commands. Doing is learning.
The first command selects the application for the function to use. The application in our lesson is Google Sheets. Our code is created within the opening and closing curly brackets. Click once after the opening curly bracket and press the return key.
Type SpreadsheetApp. Note the upper and lower case letters. This is called a class. We have instructed the function to use the SpreadsheetApp class to call the spreadsheet program.
We begin with a chain of connections to other classes. The first step is to call the spreadsheet application class. The next step is to call the active spreadsheet. The active spreadsheet is the one we are working on. Type a period followed by the word get.
The Apps script editor is helpful. It provides a list of available classes that relate to the spreadsheet app.
We want to get the active spreadsheet. We can continue to type the command or use the down arrow key on the keyboard to select the class we need. Continue typing getActiveSpreadsheet. The getActiveSpreadsheet class is the only one that is left. Press the Return key to finish selecting the class.
We want to get a specific sheet in our spreadsheet. The sheet with the date information is on the sheet named sensor data. Type a period followed by the word getSheet. We want to get the sheet by its name. Make sure getSheetByName is highlighted and press the Return key.
The name of the sheet we want to use needs to be placed within the parenthesis.
Type ‘sensor data’ within the parenthesis. Include the single quotations around the sheet name.
We are going to end this part of the code here. Type a semicolon at the end of the code. The purpose of this line is to select the sheet we want to use.
Return to the beginning of the line. Type var ss = at the beginning. This creates a variable called ss. The active spreadsheet and sheet information are placed in the variable ss.
Go to the line below this code. We are going to use the variable we created to perform the next step.
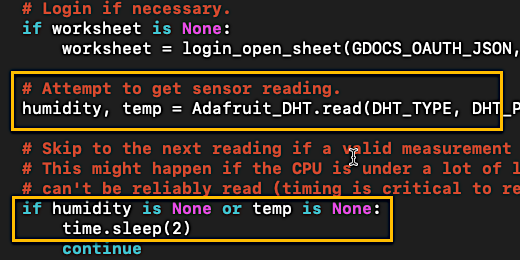
Take a look at the spreadsheet and the sensor datasheet. We want to set the split function in the first cell. The first cell for the split function is B2. The function is already here. The goal is to replace the function in the cell with the code we are creating.
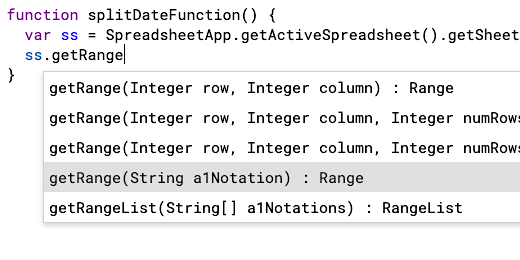
Type ss.getRange. The ss variable is used to get the range in the sensor datasheet. There are several Range options.
We want the range that gets a range using string notation. String notation is used when referencing a cell with a letter and number. Use the down arrow key and highlight getRange(String a1Notation). Press the Return key.
Replace the notation within the parenthesis with B2.
Type a period followed by setFormula. Use the class setFormula(String formula).
The spit function goes inside the parenthesis. Type (‘=split(A2,”T”)’).
Finish this line of code with a semicolon. Press the Return key to add another line.
We want to determine the last row with data. There is a class to do this for us. We are going to store this information in a variable.
Type var lastRow = ss.getLastRow();
This gets the last row with data in the data sensor sheet. The location is stored in the variable lastRow.
Press the Return key for the next line of code. We need another variable for the cell range from the first cell to the last. This Range information will be used to place the split function into each cell in the range.
Type var splitRange = ss.getRange. There are several Range options. We want the second option.
We need to identify the starting row and column for the first two parameters. The third parameter is for the number of rows to select.
Go to the piweatherData spreadsheet. The function to split the date and time is in the second row and second column.
Place the number 2 for the row and column parameters.
The parameter for the number of rows references the total number of rows with data. We have this value in the variable lastRow. Replace numRows with lastRow. Finish the line with a semicolon.
Press the Return key for a new line. Type ss.getRange(“B2”).copyTo(splitRange);.
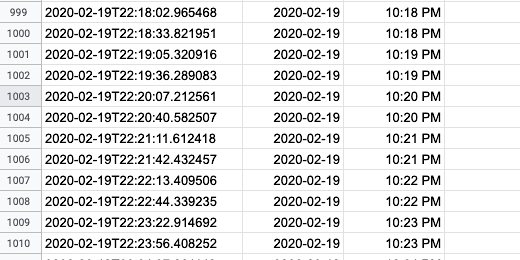
The variable splitRange contains the cells beginning at cell B2 and ending with the last row with data. The Range information is something like B2..B1036. In this example, B1036 is the last row with data.
This line gets the function we placed in cell B2 and copies it down the column to the last row with data.
The code is done. All we need to do now is run it. Before running the code we are going to check and make sure there are no errors. Make sure all the lines end with a semicolon. Check the spelling of all the commands and variables. Commands and variables are in different colors. The colors will give you a hint if there is something wrong.
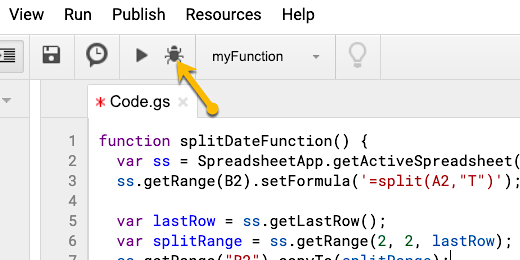
The editor has a program checker. It is called the debugger. The button has a bug for an icon. Click the debugger icon.
The debugger needs to run the code. Google needs your permission. Click the Review Permissions button.
Click the account used for the spreadsheet and script. A message appears informing you that the app isn’t verified with Google yet. Click the advanced link.
It references the name of the function that will run. Click the Go to splitDate link.
Click the allow button so the function we created can access the spreadsheet in Google Drive. No error messages will appear if everything goes well. If there are error messages you will need to check the code for mistakes. Run the debugger until you find all the mistakes. Check the cell references in the function.
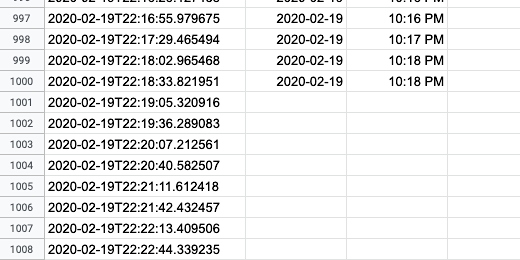
Here is my sensor datasheet. The date and time information is split up until the 1000th row.
Click the Play button in the script editor button bar.
The date and time information is split down the column until the last row with date information.
Update Fahrenheit conversion
Our Fahrenheit conversion is suffering from the same problem. The last conversion took place on the 1000th row. We need to automate the conversion here too.
Coding might be a challenge to learn at first but it makes the creation of tasks easier. In this example, we don’t need to write a new script to handle the Fahrenheit conversion. We will use the same function and adjust it to fit our needs.
Return to the code editor. Highlight the function from the word function to the last closing bracket.
The code in my editor works fine but isn’t formatted properly. The function name is indented a couple of spaces. The rest of the code is out-dented within the function. It should be the other way around. Press the Tab key while the code is highlighted. This instructs the editor to format the code. The code within the function is indented within the function. Yup, another teachable moment.
Keep the code highlighted and copy the code. The menu doesn’t have a copy option. You will need to use the keyboard commands Control+C or Command+C. Click once after the last closing bracket. Press the Return key twice. Past the code. Press Control+V or Command+V to paste.
We have two functions that do the same thing. Change the function name from splitDate to fahrenheitConvert.
The Fahrenheit conversion is in the same sensor datasheet. We don't need to change this line of our code. The conversion formula is in cell E2. We need to change the getRange parameter to E2.
Change the formula in the setFormula parameter to =D2*9/5+32. Change the single quotes to double-quotes.
The formula is in the second row and fifth column. Change the column parameter in the splitRange variable to five.
Change the getRange parameter in the last line from B2 to E2. Click the save button.
We have two functions now. We need to select the new function before running it on the sheet. Select the fahrenheitConvert function.
Click the Play button. The conversion formula is copied to the remainder of the cells. We didn’t run the debugger here because the changes we made won’t be caught by the debugger.
Triggers
The process is semi-automated. The code will update the formulas in the cells. This still requires that we open the spreadsheet, open the code editor, and press the play button. The goal is to completely automate the process so the formulas are updated on a regular basis.
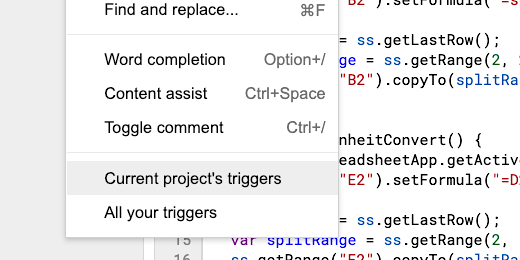
Google has an automation process called triggers. This is similar to a process we will use in a future lesson to schedule the Python script. Click Edit in the code editor. Select "Current project's triggers".
A tab is opened to the right of the code editor. This tab is opened to the Google Apps Scripts triggers portal. We are going to create a trigger to schedule the functions.
Click the Add Trigger button. It is found in the lower right corner of the page.
A trigger configuration panel opens. The triggers are linked to our Google account. Any function created under the account is available as a trigger. The splitDate function is selected.
Click the selector to reveal the other function. Leave the splitDate function selected.
Go to the Select event source option. Click the selector and choose Time-driven.
The options update with selectors for the time-based trigger.
A thousand rows will hold data for 42 days when we update the data every hour. This is enough for about six weeks. I have done some rounding in my math. It is actually 41.66 days.
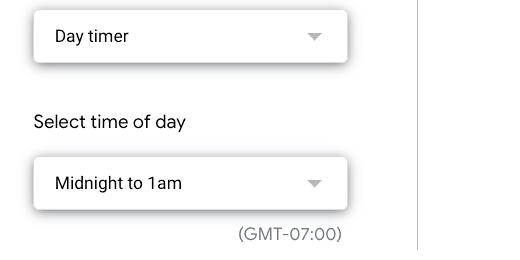
There are several trigger options. I don't want to schedule it too often. I don't want to schedule it where days go by without an update either. If I schedule it on a weekly basis the extra decimal place will eventually catch up with me. This is why I am choosing the daytimer option.
The daytimer option includes a time of day selector. The time is set to between midnight and 1 am every day. This is fine.
There is one more option. This option is a notification. The trigger will send me an email confirmation. Leave this notification option alone. Click the Save button.
The trigger portal is updated with the trigger we created.
We have two functions to run in our sheet. We need another trigger to run the Fahrenheit conversion function. Click the Add trigger button. Select the fahrenheitConvert function.
Set the trigger to be time-driven. Set the trigger to run on a daily basis. Click the save button.
The trigger’s page updates with our second trigger.
The triggers are set and we don’t have to worry about running the functions manually.
Modified functions and trigger
We have two triggers running on the same spreadsheet. These triggers are set to run on the same days and time. This is not the most efficient way to do this. Ideally, we should have one trigger for both functions if they are going to take place on the same date and time.
Return to the code editor. Click after the last line and press the Return key twice.
We are going to create a function that runs the other functions. This is one of the purposes of functions. Type function updateFormulas(){ and press the Return key twice. Place a closing curly bracket on the second return.
Type this between the curly brackets. Type splitDate(); and press the Return key. Type fahrenheitConvert();. Click the save button.
Return to the triggers tab. We don't need both triggers now. Hover over the first trigger. There is an action menu on the right. Click the menu and select Delete trigger.
Click the Delete Forever confirmation.
Hover the mouse over the remaining trigger. Click the pencil icon to edit the trigger.
Click the function selector. Choose the updateFormulas function. Leave everything else the same and save the changes.
Cancel the edit and refresh the triggers page if you don’t see the function appear in the list.
We have one trigger that runs both functions.
That ends our exploration of Google Apps scripts and Triggers. The next lesson jumps into the charts and gauges for our data.
Weather Station Project: Lesson 7
Before we organize the data we need to attend to some formatting. The date and time recorded in the spreadsheet look a little confusing. We will format the date and time information. Google sheets have functions to split the information into cells. We are going to use this function to split the date information into date and time columns.
Introduction
The Python script is getting data from the sensor. This data is being sent to a Google sheet. In this lesson, we will organize the data. The data will be used to generate temperature charts.
Before we organize the data we need to attend to some formatting. The date and time recorded in the spreadsheet look a little confusing. We will format the date and time information. Google sheets have functions to split the information into cells. We are going to use this function to split the date information into date and time columns.
The python script is sending the temperature information in degrees Celsius. We will convert Celsius to Fahrenheit. The temperature will be represented in both formats in our published charts. The data will be represented using line charts and gauges. That is the subject of the next lesson.
Formatting date and time
The date and time information in the spreadsheet is sent by the Python code in isoformat. The date and time information in one cell. We are going to separate this information. The data is missing headings.
We will add headings to help identify the date, time, temperature, and humidity.
The data in our spreadsheet is live. I don’t like to interfere with a sheet that is collecting data. We will create another sheet in the same spreadsheet. This sheet will be used to format and organize the data.
The sheet name used for our live data is Sheet1. There is a plus button on the far left where we see the sheet name. Click the plus to create another sheet.
The new sheet is created and placed to the right of the current sheet. The sheet is titled Sheet2. We are going to rename the sheet. Click the triangle next to the sheet name.
Click the rename option.
Change the name to sensor data.
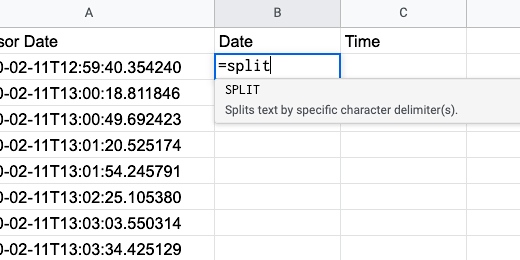
Click once on cell A1. Type Sensor Date.
Click on cell B1 and type Date. Click on cell C1 and type Time.
Click on cell A2. We are going to import the sensor date and time information from Sheet1. We are going to use a function called a Query. To use a function we use the equal sign. Type the equal sign followed by the word query.
We need to provide some basic information in the query. The information provided in the query is the query parameters. We need to identify the location of the data to query. Parameters are enclosed in parenthesis. Type an opening parentheses.
Google Sheets supplies a helpful information box that identifies the three basic parameters.
The information is in Sheet1. Type Sheet1 followed by an exclamation mark. For example, =query(Sheet1!,. This parameter is case sensitive. Make sure you begin with a capital letter S.
The data begins in the first column and row. Type the cell location. The cell location is A1. All of the information we need is in the first column. Type a semicolon followed by the letter A. We have selected the range for our query. Finish the selection by typing a comma after the letter A. This is what the query should look like now, =query(Sheet1!A1:A,.
The parameter begins with cell A1 and selects everything in column A.
The second parameter instructs the query of what information to use in the range. There is only one column of data in our range. We still need to identify what to select. Type "select *" followed by a comma. This instructs the query to select everything in the range A1:A. The asterisk is used to identify everything. It is referred to as a wildcard in searches. The comma identifies the end of this parameter.
The last parameter identifies if the data has a header. A header is a title at the top of the column. Our column does not have a header. Type a -1 and finish the query with a closing parenthesis. If the data had a header the value would be the number 1 without the minus sign. Press the return key to run the query.
Splitting date and time
The date and time information flows in from Sheet1. This information is continuously updated from Sheet1.
The date and time information spills over into column B. Move the mouse between the column A and B headers. Click and drag to the right when the pointer changes to an arrow pointing to the right.
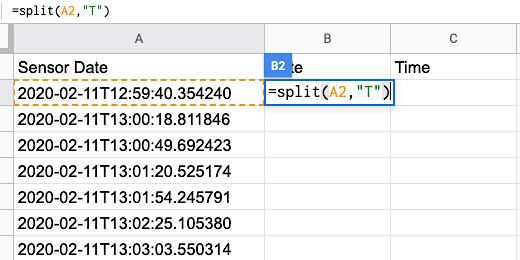
Make sure column B is clear. Click on cell B2. We are going to use another function to split the date and time information. Type the equal sign followed by the function name split.
The split function needs parameters. Type an opening parenthesis. The first parameter identifies the location of the content to be split.
Type A2 followed by a comma. You will see that cell A2 is surrounded by an orange marque.
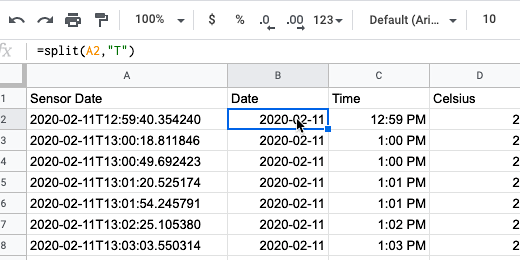
The second parameter identifies a delimiter. A delimiter is a character like a comma or a tab. The date and time information is separated by a letter. This is the letter T. The letter will be our delimiter. Type the letter T between quotation marks. Finish with a closing parenthesis. Press the return key.
It is rare to have a delimiter like T. Most delimiters are commas, tabs, spaces, or semicolons.
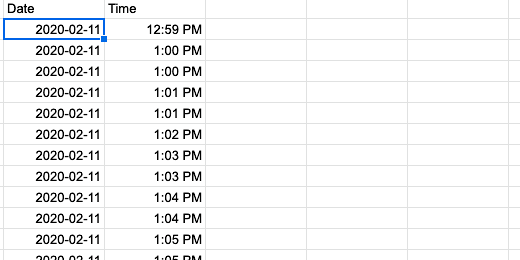
The date appears under the date column. The time is split over to the Time column.
Formatting date and time
The date information is formatted with the year first. This is followed by the month and date. The time includes the hour, minutes, and seconds. I think that the hour and the minutes are fine. We don't need seconds.
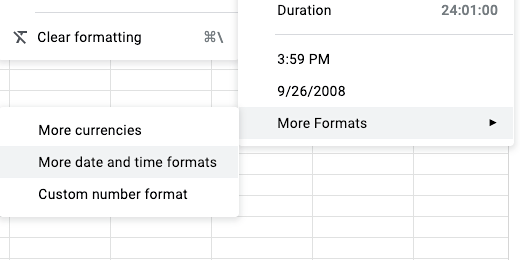
Click on cell C2. Click Format. Go down the list of options in the secondary menu. The available time format includes seconds. We need to create our own formatting to exclude seconds.
Move the cursor all the way down to the last item. The last item, More Formats, has an additional menu option. Select More date and time formats.
Find the format that has the hour and minute followed by a PM. Click on this option and then the Apply button.
We need to copy what we just did to the rest of the cells in the columns. Click on cell B2. The selected cell is surrounded by a blue outline. There is a tiny square in the lower right corner. Move the mouse pointer over the square until the pointer changes to a plus symbol. Double click the square when the cursor changes.
The date and time are copied down the columns.
The function is copied all the way down. An error appears after the last row. This is fine. The errors are resolved as new date information appears in column A.
The time formatting isn’t copied. We are going to select the entire column and then apply the formatting. Click once on the column C header. The header turns grey and the cells in the column are all highlighted.
Click Format on the menu. Go down the list of format items. The menu keeps track of the latest formats applied. Select the time format we used earlier.
Temperature conversion
We are going to query the temperature information in the next column. Type Celsius for the column title.
The query is identical to the query we used to import the date information. The data is in column B of the sensor datasheet. Go to cell D2 and type =query(Sheet1!B1:B,"select *",-1).
There are various units of measure to represent temperature. The two most common are Celsius and Fahrenheit. The data from the sensor is represented in degrees Celsius. We will convert this temperature to Fahrenheit.
Fahrenheit was proposed in 1724 by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit. The temperature is represented by the degree symbol followed by the capital letter F. Zero degrees in Fahrenheit is the point where a solution of water and salt freezes. This solution is called brine. Removing the brine from the water raises the temperature at which water freezes. Water without brine melts at 32-degrees Fahrenheit. The boiling point of water is 212-degrees Fahrenheit. The difference between the freezing and boiling temperature is 180-degrees. This information is important in our conversion.
Celsius is named after the astronomer Andres Celsius. Celsius measures zero where water freezes. The boiling point of water is 100-degrees celsius. Celsius is used when measuring temperature all over the world. The United States is the only country to still use Fahrenheit. This is why we are converting the temperature.
Understanding how the temperature scales were developed is key to understanding how to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit. To calculate Fahrenheit from celsius we multiply by 9 and divide by 5. We then add 32.
Here is how the formula came about. We add 32 because water melts at 32 degrees Fahrenheit. In Celsius, the temperature of water freezing is set to zero. Water freezes the same way. Each unit chooses to represent the freezing temperature of water at different units.
Why do we multiply by 9 and divide by 5? The scales don't rise and fall at the same rate. The difference is due to the different freezing and boiling points. The boiling point of water on the Fahrenheit scale is 212-degrees. The boiling point on the celsius scale is 100-degrees.
We actually multiply by 180 and divide by 100. These are large numbers to multiply. The degrees are a ratio. Ratios are expressed as fractions. The fraction in this equation is 180/100. We reduce the fraction to 9/5. This is an easier fraction for multiplication and division.
Here is an example. A temperature reading from the sensor is 20-degrees celsius. Multiply 20 by 9. Divide the product by 5 and add 32. The temperature in degrees Fahrenheit is 68.
Type Fahrenheit for the title in cell E1. Go to cell E2 to enter the formula. Formulas begin with an equal sign. Just like functions. Type the equal sign followed by D2. This references the value in cell D2. A number appears above the cell. This is giving us live feedback on our equation.
The multiplication symbol is usually represented by the letter x or a dot •. We don’t use these symbols in spreadsheets or coding. The asterisk, * is used for multiplication. Type an asterisk followed by the number 9.
The division symbol is /, a forward slash. Type the forward-slash followed by number 5.
Type the plus sign followed by the number 32. The preview of our equation’s answer is 68. This agrees with the example we used earlier. Press the Return key.
Click on the cell with the equation we created. Double click the square in the lower right corner to copy the equation to the rest of the cells in the column.
Humidity
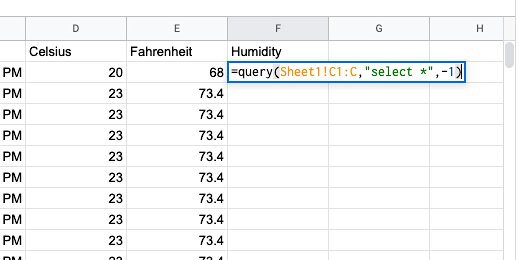
We are going to query the humidity information into the next column. Type Humidity for the title in cell F1. Use this query to bring in the humidity data. =query(Sheet1!C1:C,”select *”,-1)
The data is ready to create the charts.
Weather Station Project: Lesson 6
I cover the process for transferring the file to the Pi using Mac and Windows. The transfer on these operating systems is done through the command line. Chromebook doesn’t a similar command for its command line. We will use our GitHub account to download the file onto the Pi.
There is a sample script that is part of the DHT package we downloaded in a previous lesson. We will modify this file to send the sensor data to the Google Sheet.
Introduction
We need the JSON file from the previous lesson. This fill will be transferred to the Pi. It will be used by our Python script to send the sensor data to the Google Sheet.
I cover the process for transferring the file to the Pi using Mac and Windows. The transfer on these operating systems is done through the command line. Chromebook doesn’t a similar command for its command line. We will use our GitHub account to download the file onto the Pi.
There is a sample script that is part of the DHT package we downloaded in a previous lesson. We will modify this file to send the sensor data to the Google Sheet.
JSON file
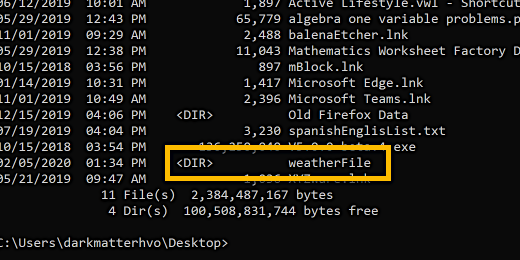
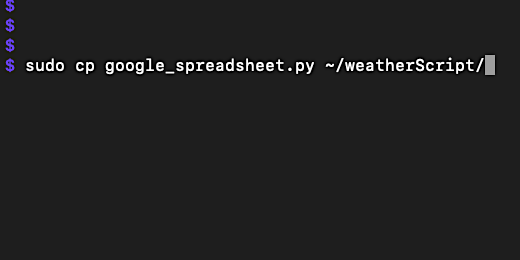
In the previous lesson, we downloaded the JSON file for our Google Sheets API. You should have placed the file into a folder titled 'weatherFile'. This file needs to be copied to the Raspberry Pi.
We are using the terminal to transfer the file with a protocol called Secure Copy, scp.
Open a terminal window. Don't log in with SSH. In the terminal, we have access to navigate the contents of our computer. I will go over the process using MacOS first.
Mac SCP file transfer
The commands on MacOS are very similar to those on the Raspberry Pi. Open the terminal application. Type ls -l to see what folder you are in.
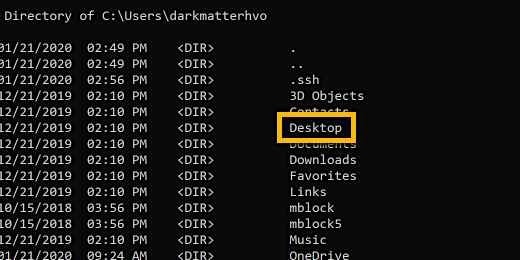
The content listed should be those of your home folder or directory. The home directory contains the Desktop folder.
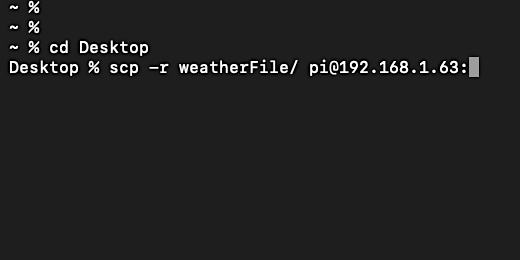
If you don't see the Desktop folder then you are probably not in your home directory. Type cd ~ and press the Return key. The tilde character instructs the terminal to switch to the home directory.
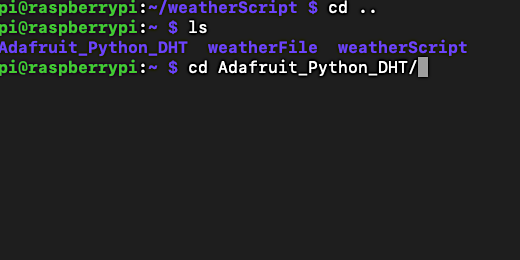
Type cd Desktop to move into the desktop directory. The folder with the JSON file should be in your Desktop folder. Type scp -r weatherFile/ pi@192.168.1.63:. Replace the IP address with the one for your Raspberry Pi. Make sure to include the colon after the IP address. The colon instructs SCP to get the directory from the current location.
Provide the password for the Pi account. The folder and file within will be transferred to the home directory of your pi account.
You will get a confirmation that the file was transferred.
Windows CP file transfer
Open the Windows command prompt. Here is a hint if you don't remember. Type cmd in the search box. Type dir to get a listing of the files and directories in your home directory.
There are several files and directories. We need to access the desktop directory. This is where we saved the JSON file inside a folder. Type cd Desktop and press the return key.
Type dir to get a listing of the desktop contents. The folder with the JSON file is in the weatherFile directory. We will copy the directory and file over to the Pi.
Type scp -r weatherFile/ pi@192.168.1.63:.
Enter the password for the Raspberry Pi.
The command prompt returns with information for the JSON file in the folder. This confirms the file and folder transfer is complete.
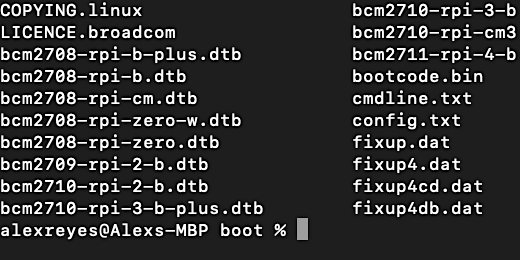
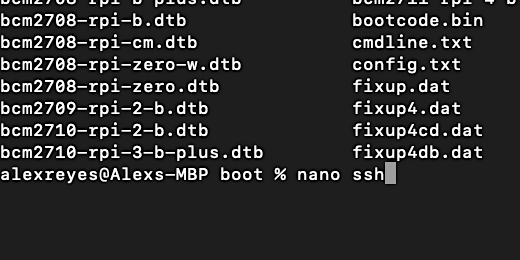
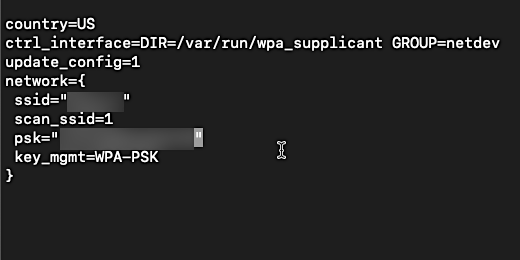
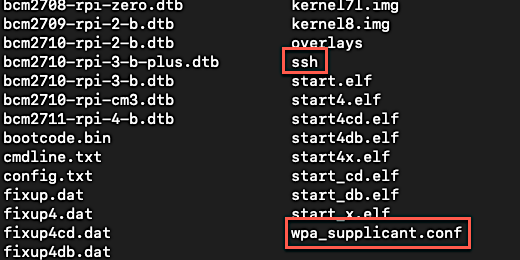
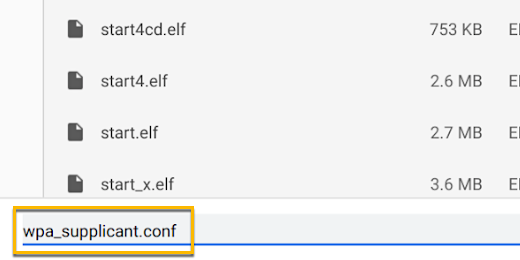
Chromebook file transfer
Chromebook don't have a way to transfer the file over to the Raspberry Pi like Mac and Windows. Well, that isn't entirely true. The latest Chromebook with access to Google Play has access to apps and extensions. Not all teachers and students have access to the latest products. I don't want to leave them out. So I have come up with an alternative.
We created a Github account in an earlier lesson. We used the account to download the sensor libraries and examples. We are going to upload our JSON file to Github from the Chromebook. We will then log into the Pi and download the file from Github.
Open the Chrome browser. Go to https://github.com and log into your account. We are going to create a repository to store our JSON file. Click the New button.
We need to provide a name for the repository. The repository name is the same as a directory or folder. This repository is tied to the account name for your Github account.
Name the repository weatherProject. Don't use spaces in the name.
Provide a description for this repository. It isn't required. It is always a good idea to document your repositories. Repositories are usually a way to share your projects with the community. In this case, we don't want anyone to have access to your JSON file. Select the option to make this repository private.
This is where we upload our JSON file. Click the link that reads uploading an existing file.
Click the choose your files link.
Open the weatherFile folder if you placed the file inside.
Select the weatherStaion JSON file and click the Open button.
The file is small. It doesn't take long to upload.
Click the Commit changes button.
The JSON file will appear in your weatherProject repository.
The repository is part of the web link in the browser address bar. This information is the path to the repository. Write this path down somewhere. You will need it soon.
When downloading a repository we see the same path.
In the next step, we are going to log into the Raspberry Pi. Click the SSH extension and select your Pi connection.
Enter the password for your Pi account.
Type git clone followed by the link to your repository. The link begins with https://github.com. This is followed by your account name and the repository name. Press the return key.
Enter the username for your Github account. We are prompted for the username because the repository is private. We need to log in to access the file. You are prompted to enter the account password after entering the account name.
The file downloads and the command prompt returns.
Type ls to verify the repository is in the home directory.
The file is in a directory with the same name as the repository. We need to change the name to weatherFile. Type mv weatherProject weatherFile.
The mv command is the move command. This is how we rename files and directories in Linux. The directory is moved and named weatherFile. The old directory is removed.
Get a list of the directory. Confirm the directory name has changed.
Weather File Directory
There are two directories in our home directory. We are going to create another directory to hold our project files. Type sudo mkdir weatherScript The mkdir command creates a directory.
We are going to copy the JSON file into this folder. Type sudo cp weatherFile/. We only need the file inside the directory. We don't remember the full name of the file but this is where Linux is helpful.
The file begins with the word weather. Add the word weather to the command. Example, cp weatherFile/weather. Press the tab key on your keyboard once.
Linux looks at files in the directory that begin with the word weather. If there is only one file then it completes the name of the file for us.
Complete the command by typing weatherScript/. Example, cp weatherFile/weatherStation-33f21afa3c11 weatherScript/.
We don't get a confirmation. Type cd weatherScript/. Type ls -l to confirm the file is in the directory.
Now we are going to work on the script to upload our data to the Google Sheet.
Google sensor script
The DHT library includes a simple test script. We used the script to verify the sensor is working. There is another example file in the directory with a sample script for uploading our data to Google. Type cd .. to return to the previous directory. The two dots refer to the directory above the current directory.
Type cd followed by the letters Ad. Press the tab key to complete the rest of the directory name.
Press the Return key to move into the directory.
Type ls -l to view the files in the directory.
The sample file is in the examples directory. Type cd examples/ and then ls -l. The file we need is google-spreadsheet.py.
We are going to copy this file to our script directory. Type sudo cp google_spreadsheet.py ~/weatherScript/. This instructs Linux to return to the home directory and copy the file into the 'weatherScript' directory.
Type cd ~/weatherScript/ so we can begin working on the script. Get a list of the files in the directory. Write down the name of the JSON file. You will need to provide this name later.
Script Google authentication
The Google script includes the lines of code we need to publish our data. Type sudo nano google, and press the tab key to complete the file name. Press enter to begin editing the file.
Use the down arrow to get to the import section. This is where we see all the hard work pay off. The import section imports all the libraries that are needed to communicate with the DHT sensor and Google Sheets. Some of the import names should look familiar, Adafruit_DHT, gspread, and the oauth2client.
Move the cursor down to the DHT type line. Move the cursor to the end of the line. Change the sensor type from DHT22 to DHT11.
The pin connection for the DHT sensor is already at 23. We don't need to change that pin value.
Move the cursor down to the GDOCS line. We need to provide the name of the JSON file. We also need to provide the name of the Google Spreadsheet. This is where you are going to need to manually enter the complete name of the JSON file.
Move the cursor with the arrow keys to the dot of .json. Press the backspace or delete key to erase the example information. Type the name of your JSON file.
Type the Google spreadsheet name in the corresponding line.
The JSON file name begins with weatherStation. A hyphen and series of numbers and letters come after the name. Make sure to include the '.json' extension. This is important. The Google Sheet name is piweatherData. That is all the information we need to provide. Let's take a look at the code and learn what is going to happen.
The code
The code will fetch data from the sensor at thirty-second intervals.
The information from the JSON file and the spreadsheet name is used to access the Google Sheet. The "Try" section of the code tries to connect to the Google Sheet with the authentication information. This authentication information is in the JSON file. If there is no success we will get a message. That is where the "except" section returns the unable to connect message.
The code will try to get the data from the sensor. If it does not receive data it will wait for two-seconds to elapse and try again.
If the sensor sends data to the program then the program will try to submit the information to the Google Sheet. It will append the data to the sheet by adding it to the first row. If it can't access the Google sheet it will wait and try again. If it can't access it at all, then it will report an error.
At the end of the loop, the script will announce that it published the sensor data to the Google Spreadsheet. It will wait for thirty-seconds and repeat the process. It will do this until we stop the program. The program is terminated by pressing the keyboard combination Control+X.
We need to save the file and exit nano before running the code. Press Control plus the letter 'o' to write the changes to the file. We are prompted to confirm the file name. Press the Return key to confirm. Press Control + x to exit the nano editor.
To run the script type sudo python3 google_spreadsheet.py.
The sensor will send data. We will get confirmation on the terminal too.
Go to Google Sheets and open the spreadsheet. The Google Sheet is accepting data from the python script. Let the script run a few minutes.
The data will remain in the spreadsheet after we have stopped the Python script. Logging out of the Raspberry Pi SSH session will also terminate the script. Keeping the script going is part of a future lesson. Stay tuned.
Weather Station Project: Lesson 5
In this fifth lesson, we will create a Google account. The account is necessary to create and enable the APIs for our project. An Application Program Interface provides a way for us to access Google services. We need access to our Google Sheets account. We also need access to Google Drive. The access permits the Python program on our Pi to send information to a Google Sheet. Google provides a special file. This file is used by our script to access the Google Sheet for our project.
Introduction
In this fifth lesson, we will create a Google account. The account is necessary to create and enable the APIs for our project. An Application Program Interface provides a way for us to access Google services. We need access to our Google Sheets account. We also need access to Google Drive. The access permits the Python program on our Pi to send information to a Google Sheet. Google provides a special file. This file is used by our script to access the Google Sheet for our project.
Google account and API
In the previous lesson, we connected the sensor to the Raspberry Pi. The Pi is collecting temperature and humidity information from the sensor. The sensor is queried every thirty-second. This information is displayed on the terminal window.
The data collected from the sensor is temporary. We need a way to collect, store, and share the information.
Google Sheets provides an easy way to share data with the world. Google has services called APIs. An API is an Application Program Interface. It provides a way to gather information from an application like Python. It shares the information with Google applications. That application is Google Sheets in our project.
The API services are free to anyone with a Google account. We need to enable and configure the services before using them. The first step is to create a Google account if you don't have one. Go over to https://accounts.google.com/signup to create an account. Log into the account.
We need to enable and set up our Google API. The API will provide the information we need in our Python code. Go over to https://console.developers.google.com. A welcome message will appear on your first visit to the developer's console. Agree to the terms and conditions and continue.
We need to create a project. Click the Project selector.
A box will open so we can select a project. Click the New Project button.
A new project page opens and suggests a name for the project.
Erase the suggested name and type weatherStation. I don't include spaces in the name on purpose. The project will eliminate the spaces for us. I like to choose how the name will appear when created.
The first letter of the first word is lower-case. The second letter of the second word is upper-case. This is a format for creating names in coding. The format is often referred to as Camel Case. Click the Create button. Don't worry about the organization's information.
The project page opens after clicking the create button. We need to enable APIS and Services. Click the button to enable these services.
An API library page opens.
Scroll down the page. Look for the Google Sheets API tile. Click the tile.
Click the Enable button.
The Google Sheets API is now enabled.
Click the Google API menu. Select the Dashboard from the APIs & Services option.
We need to enable one more API. Click the button to enable APIs and Services.
Click the Google Drive API tile. Enable the Google Drive API. Return to the Dashboard once the Google Drive API is enabled.
We are going to create credentials in our Google Sheets API. These credentials authorize the app on our Raspberry Pi to access a Google Sheet. Select the Credentials option.
Click the Create credentials button.
Select the option to create a Service account key.
Click the Service account selector.
Select the option to create a New service account.
Provide a name for the service account. Enter the name "piweatherStation".
The name is part of a service account that is similar to an email address. The service account ID is piweatherStation@weatherstation. I have hidden the rest of the information for security reasons. The rest of the address includes numbers and letters. It ends with the .com extension. We will need this information later.
Click the Role selector and choose Editor from the Project option. Click the create button.
A file is created with the credentials information. This file is downloaded to your computer. It downloads right away on the Chrome browser. Other browsers will prompt you to confirm the download.
An information message appears on the page. Close the message. The information in this file is for your account and Sheets API. Don't share it with anyone.
The JSON file is an acronym for JavaScript Object Notation. This file allows us to access the Google Sheet and send it information from our weather station. Create a folder on your computer desktop and title it "weatherFile". Place the JSON file inside this folder.
Chromebook users will create a folder in the download folder and leave the file here for now.
Don't close the Google Developers Console. We need information for one of the steps in the next lesson.
Weather datasheet
Our next step is to create a spreadsheet to receive the data. Open a new tab. Go to https://sheets.google.com. Click the Blank tile to create a new empty spreadsheet.
Click in the untitled spreadsheet name. Name the spreadsheet "piweatherData".
I know we are not including spaces in our files. Using this naming convention makes things so much easier later.
We need to share this spreadsheet with the API account we created in the last lesson. Click on the Google Developer's Console tab.
We are going to drill down from the beginning to get the information we need. I am doing this for those of you that might have closed the tab. I also want you to know where the information is for future reference.
Go to https://console.developers.google.com and login if requested. Click on Select a project. The link is next to the Google APIs logo.
If you didn't log out then you will see the weatherStation project in the project selector. Click the weatherStation API link.
Click the weatherStation project API link.
We are taken to the weatherStation Dashboard. Click on the Google Sheets API link at the bottom of the dashboard page.
Click the credentials link.
Look for the service account piweatherstation email account. Click on the link to open the account settings.
The email appears on the settings page. Highlight the email. Right-click and copy the email.
That's all we need for now. Return to the Google Sheets we just created. Click the Share button.
Right-click inside the email field and select paste.
Leave account with edit permissions. Click the send button.
We are done with the APIs and Google Sheets setup. We will return our attention to the Raspberry Pi in the next lessons. Keep the JSON file on your desktop on Chromebook download folder. It will be used in the following lessons.
Weather Station Project: Lesson 4
In this lesson, we connect the DHT 11 temperature and humidity sensor to the Raspberry Pi. The sensor is attached to a breadboard. Leads are used to connect the sensor pins to the GPIO pins on the Raspberry Pi. On the Pi, we download the DHT sensor library from Adafruit. The library has an example code to test the sensor. We will edit the example to read the sensor information.
Temperature and humidity sensor
Introduction
In this lesson, we connect the DHT 11 temperature and humidity sensor to the Raspberry Pi. The sensor is attached to a breadboard. Leads are used to connect the sensor pins to the GPIO pins on the Raspberry Pi. On the Pi, we download the DHT sensor library from Adafruit. The library has an example code to test the sensor. We will edit the example to read the sensor information.
Connecting the sensor
The temperature and humidity sensor is in the Elegoo Adruino kit. The sensor is model DHT11. This model number is important We will refer to it a few times in this lesson. The sensor is shown in the image below. The sensors themselves are enclosed within the blue plastic cover. The bottom of the sensor has three connectors. One connector receives power from the Raspberry Pi board(vcc). Another connector sends information to the Pi(data). The third connector is the ground connector.
The kit comes with a CD that contains information and resources for the modules and sensors. Most computers don't come equipped with a CDROM. To get the information for the DHT11 sensor we need to use the Internet. The information for the sensor is found using the link below. I have replicated some of the important information we need for the project.
http://www.circuitbasics.com/how-to-set-up-the-dht11-humidity-sensor-on-an-arduino/
The first pin on the left connects to the Raspberry Pi's GPIO pin. It outputs both temperature and humidity information. The second pin is referred to as the Voltage at the Common Collector, Vcc pin. The sensor module accepts voltages ranging from 3.3 volts to 5.5 volts. The third pin is the ground pin.
The breadboard
We need a breadboard to connect the sensor to the Raspberry Pi. The Elegoo kit contains a solderless breadboard. It looks like the image below. A breadboard contains a series of holes. The holes are organized into columns and rows. On either side of the breadboard are red and blue lines. The red lines have a plus symbol at either end. The red lines have a negative symbol at either end. All the holes along the red line are linked to each other. The same is true for the holes along the blue line. These are used to provide electric current for circuits. They are referred to as the negative and positive rails. This is because they are like the rails of a train track.
There is a groove down the center of the breadboard. It is often referred to as the trench. This divides the connections on the breadboard. This is also the reason why there are two sets of red and blue lines.
The columns for the holes between the rails are labeled with letters. The holes in these columns are not connected down the column like the negative and positive rails. The holes are connected in rows. For example, the holes from row a to e are connected. One row does not connect to another row.
The wires from the sensor plug into the holes on the breadboard. Handle the sensor carefully. You should use the static strap when handling any sensor. Get the sensor module and plug it into the breadboard. Each sensor connector goes into a separate hole. Each hole needs to be part of a different row. I recommend placing the sensor module in the center of the board along column 'a'. The sensor module in my image is between rows 25 and 35. Plugin the sensor so the blue sensor housing is facing the center of the breadboard.
Lead wires
In the kit, you will find several wires. These are called Lead wires. They are used to make connections between electronic components or modules. There is a bundle of long lead wires. One end of each wire has a pin. The other end has a receptor for a pin. The wires are joined together but they are easy to separate. You need three lead wires. Get a red, green, and black wire. Red wires are used to identify connections to electric current. Green wires are used to identify connections to ground. Black wires are used for data but we can use any color for the data.
Get the pin end of the black lead wire. Plug it into one of the holes in the row for the data pin on the sensor module. Remember, all the holes in a row are connected.
Get the pin end of the red lead wire. Plug it into the row for the Vcc pin on the sensor.
Get the pin end of the green lead wire. Plug it into the row for the ground pin on the sensor module.
Raspberry GPIO pins
We are going to connect the sensor to the Raspberry Pi. Make sure the Pi is shut down and the power source is disconnected.
Pins are sticking out of the Raspberry Pi. These are referred to as GPIO, General Purpose Input/Output pins. There are 40 pins.
The pins are not labeled on the board. To know which pins to use we need to look at the pinout key for the board. I have created a pinout table for the board. The image of the table and bard is shown below. The table represents the various voltage, ground, and GPIO pins. I have drawn lines for the pins we are using to connect the sensor module.
The first pin at the top of the board is pin 1. This pin provides 3.3 volts. The pin next to it provides 5 volts. Our module is capable of using 5 volts. Most lessons with this module use 3.3 volts. The ground pin is on number 6.
The voltage and ground pins are different from GPIO pins. GPIO pins do not provide voltage. They send and receive information.
There are several GPIO pins to use. I chose to use GPIO23.
Connect the other end of the lead wires from the sensor to the corresponding pins on the Raspberry Pi. Red goes to pin 1, green to pin 6, and black to GPIO23.
Make sure the Raspberry Pi is not powered on. Never connect or disconnect any circuit to the Raspberry Pi while it is powered. Doing so could damage or destroy the Raspberry Pi. It could also damage modules and sensors.
Get the micro USB power cable for the Raspberry Pi and plug it in. You can connect the Raspberry Pi to an external display if you want. There is no need because you won't see anything. Everything is done and viewed through the SSH terminal window. Wait until the green light on the Pi stops blinking before attempting to log in with SSH.
DHT sensor packages
We need to install the DHT sensor packages. These packages are used by Python and our code to retrieve data from the sensor module. Type sudo pip3 install Adafruit_DHT. The packages are created and maintained by Adafruit. Adafruit creates and sells a variety of sensors and modules for Raspberry Pi and Arduino.
Sensor libraries
There are some libraries available to help us get started. Libraries are resources to help make the process of connecting top sensors and other components easier. The libraries include some examples for using the DHT sensor. One of these examples includes the code for accessing the Google Sheet for our data. Using this example will save us some time.
To get the files we need to set up a free GitHub account. GitHub is an online repository for storing, sharing, and distributing code. It is used by millions of develops to store their projects and share them with the world.
You don't need to be a programmer to get a GitHub account. Although, with all the work you have done so far I think you qualify. Go over to github.com and create an account. All you need is an email address. Remember the username and password for the account. We are going to need it in the next few steps. Keep the browser open and remain logged into the account.
We need to install the Git service onto the Raspberry Pi. Type sudo apt-get install git -y. This is similar to previous installations. The final command in the line includes '-y'. This is a command-line flag. When installing packages we are often prompted to confirm the installation. The process stops and waits for our response. The '-y' instructs the installation service to agree to the installation for us. This saves some time.
After the installation is complete we need to configure our account to retrieve content from Github. Type git config --global user.name "Your Name". Replace "your name" with the username created in the Github account. Leave the quotation marks don't erase them. You won't get a response unless the username is wrong.
Type git config --global user.email email@example.com. Replace email@example.com with the email used to create your Github account. You don't need the quotation marks for the email information. That is all there is to it.
We are ready to download the Adafruit DHT libraries. We need the address to the libraries in Github. The libraries are available from this URL, https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_Python_DHT. Copy this link. Paste it into the command line after typing git clone. Type git clone https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_Python_DHT.
The library is downloaded and saved to the Pi account home directory. We haven't looked at the home directory yet. Type ls -l to get a listing of the items in the home directory.
There is one directory. This is the DHT-sensor-library. A directory is like a folder. We know this is a directory because of the letters displayed on the right. The directory information contains letters that identify the permissions available for the directory. The letter d identifies this as a directory. The letter r means we have permission to read or see the contents. The letter w means we have permission to write or change the contents. There are several levels of permissions. That is all we need to know for now.
Reading sensor data
The repository library we downloaded from Github contains some sample files. One of these sample files reads information from the sensor. We are going to open the directory to see the sample file. Type cd Adafruit_Python_DHT/. The cd command is used to change the directory. Think of it as opening a folder on your computer. We are moving from our home directory into the DHT library directory.
Type 'ls -l' to see a listing of the files in the folder.
There is another directory named examples. Type 'cd examples/'.
Type 'ls -l' to get a list of the items in the directory.
We are going to use the simpletest.py file to get information from the sensor. Before using the file we need to make some modifications to code in the file. We will use a text editor that runs from the command line. The text editor does not have a graphical user interface like modern editors. Use arrow keys and keyboard commands to move around.
To open the file for editing we type the name of the text editor followed by the name of the file to edit. The name of the text editor is called nano. This is not the only text editor but it is one of the easier ones to use for those new to command-line editors. Type 'nano simpletest.py'. The '.py' is the file extension and identifies this as a Python file.
The command-line screen is replaced by the nano text editor. There is a lot of commented text at the beginning. This commented text is information regarding the file. The cursor appears at the top of the text file on the first line.
The '#' is used to comment text. This text is different from instructions sent to the Pi or sensor. It is usually information that documents what the code does. Most programmers thoroughly document their code.
cursor location at the beginning of the file
Use the down arrow key on your keyboard to move the cursor to the line that begins with the word sensor. This line identifies the sensor we are using. The sensor is currently set to the DHT22. This is a newer version of our sensor the DHT11. I will go over the differences in a future lesson.
Use the right arrow key to move the cursor to the end of the line.
Press the backspace key on Windows or the Delete key on Mac to erase the number 22. Type the number 11 after DHT.
Use the down arrow key to move the cursor to the line that begins with the word pin. The cursor moves down the lines relative to its last position. This is why the cursor rests at the end of the line.
The code in this example is set up to work with a different device. The PIN is set for that device. The device is called a Beaglebone. Our device is the Raspberry Pi. To work with our Raspberry Pi we need to change the PIN. The sensor is connected to GPIO23. Erase the pin information and type the number 23.
The commented information provides information for providing the number when using a Raspberry Pi. This an example of documentation by the programmer of this example.
Move the cursor to the bottom of the text file. The last few lines are what retrieves the data from the sensor. The instructions get information from the sensor.
The first line, if humidity is not None and temperature is not None:, checks to see if the sensor is sending data. The 'not None' is asking if there is something.
The second line has several components. It prints the temperature and formats it using from the instructions.
The code “print ( 'Temp = *c” instructs Python to show the temperature with one decimal value. The number one after the decimal point sets the number of decimal places. The letter 'f' is used to format the number as a floating-point value. This means the value includes decimals. The letter 'c' returns the temperature in Celsius.
Floating-point values are used when the number contains decimals. Numbers that do not use decimal values use Integer values.
The code “Humidity = %” displays the humidity value with one decimal place value. The percent symbol is used to represent the value as a percentage.
The “.format(temperature, humidity)” describes the order in which the information is to be displayed.
The last line runs if there is no information from the sensor. A message appears and the code returns to the beginning and listens for information from the sensor. If everything goes well we will not see this line.
We need to save the changes. The bottom of the editor provides information on how to do that. The little arrow symbol next to the letters represents the Control key on your keyboard. To save the information we press the Control key and the letter 'o' at the same time.
The name of our text file appears. We are asked to confirm that we want to save changes to the file. Press the Return key to confirm. This is similar to File and Save as in a word processor.
Press the Control key and the letter 'x' to exit the editor.
We are returned to the command line. To run the program we need to type the application and the file to be opened. Type 'python3 simpletest.py'.
The program responds with the sensor data. In my example, the temperature is 24 degrees Celsius. The humidity is 22 percent.
The script will continue to return the sensor temperature and humidity information every 30 seconds. The script contains a loop that continues until we stop the script. Press Control+C to stop the script. The command prompt will display after the last reading.
Run the script again at anytime by typing the same command.
Don’t forget to shutdown the Raspberry Pi before disconnecting the power. Log back in if you forget to shutdown before quitting the SSH terminal session.
If the sensor does not work then here are some things to try. Make sure the connections are correct. The lead wires on the sensor should be firmly in place. The lead wire colors from left to right are black, red, and green. The red wire is on pin 1 on the Raspberry Pi to receive 3.3 volts. The green wire is on pin 6. The black wire is on GPIO23. This is physical pin 16.
If it still doesn't work then check the simpletest.py file. Use the nano editor to open the file. Make sure there are no stray characters. Make sure everything is typed correctly. Save the file and try again.
Weather Station Project: Lesson 3
This is lesson three of our weather station project with a Raspberry Pi. In these lessons, you will learn how to Find the Raspberry Pi’s IP address Login into the Pi with SSH Update the Pi location and time zone Update the Raspbian operating system Install applications and services Shutdown the Raspberry Pi
Introduction
In these lessons, you will learn how to
Find the Raspberry Pi’s IP address
Login into the Pi with SSH
Update the Pi location and time zone
Update the Raspbian operating system
Install applications and services
Shutdown the Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi connection
The Raspberry Pi has connections for a display. The USB ports are used to connect a keyboard and mouse. The weather station does not need a display, keyboard, or mouse. For these lessons, we are going to connect a display. This gives us a sense of what is going on. It is useful for first-time users to get some visual feedback. Connect an external display to the Raspberry Pi with an HDMI cable. Don't connect a keyboard or mouse.
We are going to run the Raspberry Pi in what is called the headless mode. This means we are not going to physically connect to the device when working with it. We are going to log into the Raspberry Pi from another computer. This is very useful because we can use any computer. The Pi will be controlled by your Mac, Windows, or Chromebook. I have instructions for each.
If you are using Raspberry pi (version 1.xx or 2.xx) without wireless capabilities you need to connect it with an Ethernet cable to a router. The Ethernet cable usually connects to a drop. This is a port on the wall. The cable is also connected to a Router. Below is an image of a wireless router and the Ethernet ports on the router. Raspberry Pi 3 and 4 with wireless capabilities don't need an ethernet cable.
Use the power adapter that came with the Raspberry Pi kit. Plug the adapter to a wall outlet. The Raspberry Pi doesn't have an independent power button. It will turn on once the Pi is connected to a power source. Plug the other end of the power adapter to the Raspberry Pi micro USB connector.
Don’t unplug the Raspberry Pi until everything is setup. Unplugging will turn off the power and crash the computer. You might need to start all over. At the very least, you will need to connect a keyboard and mouse to the Pi and fix some issues.
A couple of lights on the Pi will turn on. A red LED indicates the Raspberry Pi is on. A blinking green LED shows there is activity on the Pi. This activity is usually from the Pi reading and writing information to the micro SD card. The green light will blink for a few minutes while the Pi boots. Eventually, the LED will stop blinking. This means the Pi is waiting for instructions from us.
What do we see on the connected display? The Raspberry Pi displays lines and lines of text as it boots. It configures everything for us. It looks for the SSH file to setup SSH services. It looks for the WPA file to set up the wireless connection. If the green LED doesn't blink and nothing appears on the display this may be because the microSD card isn't properly inserted. Check the card to make sure it is properly inserted.
Unplug the power supply to the Raspberry Pi before checking the microSD card.
Raspberry Pi IP address
We need to know the IP address for the Raspberry Pi. This is needed to log into the Pi with Secure Shell, SSH. I reviewed the process for getting the IP dress using Mac, Windows, and Chromebook. All three use their version of the command line.
Mac Terminal IP address lookup
As long as your computer is part of the same network we can look up the IP address of the Raspberry Pi. Open the Terminal on Mac or Windows and type this command, ping -c 3 raspberrypi.
This command sends a chunk of information to the host identified as raspberrypi. It looks for this host on the local network. Once it finds the host it sends information to confirm the host is communicating with the network. The ping identifies the IP address of the host. The IP address for my Raspberry Pi is 192.168.1.63. Look at the IP address for your Pi and write it down. There is a parameter between the ping command and the hostname. This parameter instructs the ping command to limit the pings to three.
The IP address will change if you move the Raspberry Pi to another location. If you do move it, run the ping command to get the new IP address. You will be moving the Pi to gather temperature and humidity information from various locations.
Windows IP address lookup
We are using the command line again to get the IP address of the Raspberry Pi. This IP address is needed so we can log into the Pi with SSH. Go to the Windows search box and type CMD to open the command line. Type ping raspberrypi.
The command will ping the network looking for the host named raspberrypi. It will send packets of information to confirm that the host is communicating. The ping command will send four packets. The IP address of the Raspberry Pi is returned. The IP address for my Pi is 192.168.1.63. Get the IP address for your Pi and write it down. You will need it in the next lesson.
Chromebook IP address lookup
The Chromebook has a version of the command line called the Chrome Shell, Crosh. Use the keyboard combination CTRL+ALT+T. A tab opens and displays the Chrome Shell prompt.
Type ping -c 4 raspberrypi. We need to enter a count for the number of pings. The command will continue to ping the Pi until we interrupt it with CTRL+C.
The ping command will look for the Raspberry Pi with the hostname "raspberrypi". It will send four packets to the Raspberry Pi. This tests the Pi's ability to communicate on the network. Part of the information returned includes the IP address for the Pi. The IP address for my Pi is 192.168.1.63. Look for the IP address of your Pi and write it down. We will need it in the next step.
During these lessons, I will use the IP address for my Pi. Please replace my IP address with the one for your Pi.
SSH Mac Login
To access the Pi we will use the SSH connection. The Pi is connected to our router and has received an IP address from the router. This is true for both the wireless and ethernet connections. The Raspberry Pi will be assigned an IP address. An IP address is a set of numbers divided into four sections of three numbers each. A typical router address looks like this, 192.169.001.122. The IP address provided to the router is unique. We need to find the address assigned to your Raspberry Pi.
Type clear at the prompt. This clears away the information in our terminal. Type ssh followed by a space and the word pi. We are opening the ssh application to login to the Pi account. This is the default account. Type the "@" symbol. Enter the IP address for your Raspberry Pi after the "@" symbol. We are instructing the SSH application to access the device at the given IP address. It will then attempt to log in with the account name "pi". Press the Return key.
The Raspberry Pi will reply to your attempt with a password prompt. The password for all new Pi accounts is “raspberry”. The password information is hidden so you won’t see the letters as they are entered. Type the password and press the Return key.
You will see the Raspberry Pi Raspbian command prompt. The latest version of macOS might return a login attempt error. In that case, you will need to use the command instructions below.
Mac SSH error
We need to clear the ssh keys on the host. Type the command below. Replace the IP address with that of your Pi.
ssh-keygen -R 192.168.1.163
Windows SSH Login
Type “cls” to clear the contents of the command window. Type ssh pi@192.168.1.63 at the command prompt. Replace my IP address with yours.
The Raspberry Pi doesn’t have any security settings enabled yet. You are prompted to confirm the connection. Type yes and press the Return key.
The Raspberry Pi prompts us for the Pi account password. The default password is “raspberry”. Type raspberry and press the Return key to log in. The password is not displayed as it is typed. This is for security reasons. Type it carefully.
The password is authenticated and you are logged in. The Raspberry Pi command prompt is ready for our instructions.
Chromebook SSH login
The Chrome Shell does not include the Secure Shell application. We need to install it. It is available in the Chrome Web store. Open the Chrome web store. Search for the Secure Shell Extension. Click the Add to Chrome button to install the extension.
Click the extension icon after the installation is complete.
Click the Connection Dialogue option.
A configuration box opens where we provide the account information needed to log into the Pi.
Type pi@ followed by your IP address into the first input box. The extension fills in the account name and the IP address for the other boxes. Press the Enter key on your keyboard.
We are prompted to allow the extension to open SSH links. Click the allow button.
We are also prompted to allow the extension to open web and SSH links. Click the allow button.
We are prompted to confirm the connection to the IP address with SSH. Type yes and the Return key.
Provide the password for the account on the Raspberry Pi. The password is “raspberry”. The password does not appear as it is typed. This is done for security reasons. Type the password and press the Return key.
The SSH extension updates with the Raspberry Pi command prompt.
The extension remembers the connection information. The extension displays this information the next time we want to connect. You still need to provide the password.
Raspberry Pi password
From this point forward everything will be related to the command prompt. I won't be jumping from computer to computer to explain different methods.
Leaving the default password set to raspberry is never a good idea. The first thing we need to do is change the password. Type passwd followed by a space and the account name pi.
The password doesn’t have to be complex. Use at least eight characters. Write the password down somewhere. We need to verify the password change by entering the old password. This would be the current password, raspberry. Type the current password when prompted.
The password will not be displayed as it is entered. Type in a new password. Press the Return key to update the password. You will be prompted to type the new password again.
Raspbian is constantly being developed and updated. Those updates aren’t always included in the installer. We need to check for updates and install them.
You might have the Pi connected to an external display. This was useful when the Pi booted. Since then the display has been silent. This will be true for the remainder of our lessons. Keep it connected for the remainder of these lessons. The final lesson covers the process of shutting down the Pi.
Configure services
We need to configure some basic services before proceeding to the next step. Type sudo raspi-config followed by the return key.
Instead of repeating the instruction to hit the return key, hit the return key after a command-line instruction.
The configuration tool is very useful. The top of the tool panel provides information about the model and version of the Raspberry Pi. The configuration tool provides a list of settings and services we can change.
Set location and time
The Raspberry Pi doesn't get and set the date and time information for the location. We need to set this manually. This information is important for sensor data. Use the down arrow key to select the localization options. Press the Return key.
Press Return to set the location information. The terminal will go blank for a few seconds. The Pi is retrieving the needed information.
A list of locations is displayed. The locations are listed in the UTF-8 format. The UTF-8 format lists the location language followed by the territory. For example, en_US is for English and United States. Select the UTF-8 for your language and country. Press the space bar to select the location. An asterisk appears in the location square.
Press the tab key to jump to the OK. Press the Return key to update the location.
You will be prompted to select a language region if applicable. In this example, I am prompted to choose between British English or American English. Select a regional language and press the Return key.
The process could take a minute or two. The terminal will update with process information.
The main menu appears when the process is complete. Select the localization options again. We are going to set the time zone next.
Select the option to change the timezone.
Use the up or down arrow key to select your country. Press the Return key.
Use the arrow keys to select your time zone. Press the Return key to mark the time zone.
The main menu will return once the process is complete.
Hostname
The hostname for the Raspberry pi is "raspberrypi". This is the hostname we pinged to discover the IP address. We must change the hostname. There are several reasons for changing the name. One reason for changing the name is that others on your network might need to set up their Raspberry Pi. Pinging the hostname "raspberrypi" will return several results. One of them is your Pi. Changing the hostname will prevent them from getting a ping from your Pi. Select network options.
Select the hostname option.
An information box provides important information regarding hostname options. We can only use letters and numbers in the hostname. A hyphen is also allowed. Press the Tab key and the Return key to continue.
The current hostname appears. Press the delete or backspace key to erase the name. Provide a name that is relevant to the Pi.
I recommend changing the hostname to "weather-pi". I use the hyphen to separate the words. Blank spaces are not allowed in hostnames. Press the Return key to update the hostname.
Press the tab key twice to select Finish. Press the Return key.
Changing the hostname requires a reboot. Proceed with the reboot. You will need to log back into the Pi after it has rebooted. Use the SSH terminal, command prompt, or extension on Chromebook.
Raspbian Updates
We need to check for available updates. The updates are available from a repository common for many versions of Linux. Raspian is a version of a Linux distribution called Debian. The repository of updates for Debian is maintained by the Linux community. Type sudo apt-get update.
The installation of updates often require administrative level permission. The term "sudo" is used to perform updates, installations, or changes as the administrator of the device. The term stands for Super User Do. Super User is another term for the computer administrator. By typing the "sudo" command we are instructing the operating system to look for updates.
The updates are retrieved and installed using "apt" service, the Advanced Packaging Tool. This application is used to update and install packages. After "apt" is a hyphen followed by the word get. This instructs the packaging tool to get the available updates for Raspbian.
The APT application connects to the repository of services for Raspbian. It begins to download a series of packages. These packages contain instructions and information for the updates available. Think of it as a list of items available for installation on Raspbian.
The process is fast. The list is ready to begin retrieving and installing updates.
To install the updates type sudo apt-get upgrade. This instructs the package tool to upgrade all the services that need upgrading.
The upgrade process takes several minutes to complete. The terminal will scroll with lines of information. This information represents the services and applications that are being upgraded. The upgrade tool on my Pi will upgrade 63 services and download 149 MB of files to perform those updates. The number of services and file sizes may vary on yours.
Before the upgrade begins we are prompted to confirm the upgrade process. Type the letter Y and press the Return key.
You can step away from the computer for the upgrade process. Return after five or ten minutes to respond to a message that will appear somewhere in the process. Type q to finish the upgrade process. You might receive other prompts. It depends on the upgrades. You might need to type yes to another prompt.
If you are looking at the Raspberry Pi on a display then all you will see is the Raspberry Pi login prompt. All the action is going on in the terminal window.
Type clear at the command prompt after the updates are done. This will clear the terminal window for the next steps.
Python and Google Services
In a future lesson, we will set up Google APIs to collect information from the weather station. To send information to the Google API for Google Sheets we need to set up applications and services.
We are using Python, a programming language to communicate between the Pi and Google’s API. We are going to update Python and some of the services. The update process is similar to the update for the Raspbian operating system. These updates don’t take as long as the updates we just performed.
I want to make sure we have them installed with the latest updates. This process is useful so that you understand what services are being used and how they got there.
Python updates
Python is a popular programming language. Versions 2 and 3 are installed on our Pi with Raspbian. Type sudo python --version. This shows version 2.7.16 is installed on my Raspbian.
We are going to use the latest version of python. Type sudo python3 --version. The version installed on my system is 3.7.3. Yours might be newer.
We need to install some additional packages for Python. Type sudo apt-get install python3-dev. This command is similar to the update command. This command includes the install parameter. The APT package tool will download and install the Python 3 development files.
Type the letter y to confirm the installation of the Python 3 development packages.
We will install the Python Package Index. This is a package manager for packages written in Python. Type sudo pip apt-get install python3-pip. Type the letter y when prompted to continue with the installation.
I want to make sure other Python services are up to date. Type sudo python3 -m pip3 install --upgrade setuptools. This time we didn't use the apt-get command. Python has services through PIP to get and install packages. Type y at the prompt to confirm the setuptools update.
Python will search for any updates to the setuptools. It will install those updates if any exist. The terminal window might not display any text for a while. This is normal.
Type sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade wheel. With this command we are now finished with our updates for Python 3. In the next step, we will install Google services for Python.
Google Services for python
Go ahead and type clear to refresh the terminal window. Type sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade gspread. This instructs the Python package installer to locate and install the gspread package.
After a few seconds, you will see the installation progress.
The “gspread” packages and Python need to communicate with the Google Sheets API. Communication takes place over secure services through Google. This installs a client package that is used to authorize our access to the Google Sheet. We need to update the secure services on our version of Python. Type sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade oauth2client.
We need one more package to access the Google Sheet API. Type sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade PyOpenSSL. Google uses secure services for all its products. This is easily identified by the ‘https://“ and the lock icon in the address bar. The Open SSL package allows us to access these services.
Shutdown
We are done with everything for these lessons. We need to turn off the Raspberry Pi. The Pi is like all computers. It needs to shut down before disconnecting.
Type ‘sudo shutdown -h now’ and press the Return key.
The display connected to the Pi shows information related to the shutdown process. It is terminating applications and processes. It is also closing files and removing unneeded temporary files.
The whole shutdown process takes a few seconds. The terminal window will display a message informing you that the SSH session is closed. You are logged out of the Raspberry Pi and the SSH application on the Pi has stopped accepting requests.
Disconnect the micro USB cable from the Pi.
Practice booting the Pi and shutting it down. This will give you a sense of how long it takes the Pi to boot and shutdown.
Weather Station Project: Lesson 2
This is the second lesson in our weather station project. These are the steps covered in the lesson. Download the Raspbian operating system (lite version). Flash the image onto the MicroSD card. Create an SSH file to access the Raspberry Pi remotely. Create a configuration file to connect with your Wifi.
Introduction
This is the second lesson in our weather station project. These are the steps covered in the lesson. Each step is covered using Mac, Windows, and Chromebook.
Download the Raspbian operating system (lite version)
Flash the image onto the MicroSD card
Create an SSH file to access the Raspberry Pi remotely
Create a Wifi configuration file to connect with your Wifi
Insert the MicroSD card into the Raspberry Pi
Download Raspian OS
The Raspberry Pi uses an operating system based in Linux. Linux is a free and Open Source operating system. Linux, in one form or another, is responsible for the Internet. Most web pages are hosted on Linux. Linux is found in many devices from home thermostats to smartphones. The Linux for the Raspberry Pi is called Raspian. It is built specifically to run on the Raspberry Pi. It is not the only version but it is the one we will be using.
The Raspian operating system was installed on the micro SD card we just erased. Why did we erase the card then? I want you to understand the process of getting a Raspberry Pi up and running from scratch. This process will help you prepare a Raspberry Pi anytime. The download process is the same for Windows or Mac.
The operating system is available from the Raspberry Pi website. Go to “https://raspberrypi.org/downloads”. Click the Raspbian button.
There are three download options. The first two are typical download options. These versions contain many resources. These resources are very good if we plan to use the Raspberry Pi as a desktop device. We don't need all these resources for our projects. The full version is over two gigabytes. The desktop version is a little over one gigabyte. We will use the lite version. This is just a little over four-hundred megabytes. The small size is faster to download and install on the Pi. We will install and update the resources we need.
Click the Download zip option.
Wait for the Raspbian file to download. Find the file on your computer. Double click the file to extract the operating system image. Place the image file on your desktop. The Raspbian image file will have a name that begins with a date. The date is followed by raspbian-buster.img. The date of my image is September 26, 2019. The date on your image file might be different. 2019-09-26-raspbian-buster.img. The image file ends with the “.img” extension.
Flashing the micro SD card (Mac and windows)
We need a special program to help us place the image onto the micro SD card. We can’t just copy the file over. The process of flashing a micro SD card with the image is important. The Raspberry Pi will not be able to boot from the card if it is not properly formatted and flashed. The flashing tool is available from Balena. Go to https://balena.io/etcher.
The process to flash the MicroSD card with Balena Etcher is the same for Mac and Windows. I have instructions for doing this with a Chromebook in the next lesson.
The site recognizes the operating system of your computer. The download button will point to the version of Balenaetcher for your computer. I will download the Mac version. Click the triangle on the button to select another download option. On Windows, I recommend using the Etcher for Windows Installer option.
Download and install the Balenaetcher app on your computer. Mac users will copy the file to the Applications folder. Windows users will run the installer. Open the application after the installation is complete.
There are three steps in the process. We need to select the Raspbian image first. We then select the micro SD card for the destination. In the third step, we begin the process of etching the operating system. Click the "Select image" button.
Navigate to your computer’s desktop and select the image file. The file will appear as the selected image. Click the Select Target button.
Find the micro SD card and select it. The disk identifier might change if you connect another drive to the computer. Verify the device by checking the storage capacity. Click the continue button.
Verify the image file and the destination drive one last time. Click the Flash button. You will be prompted on Mac to enter your Admin password to authorize the flash process. Windows will ask you to confirm that you want Belenaetecher to modify the drive.
The Flash process takes several minutes. Don’t interrupt the process. The image will be Flashed onto the drive and verified. The verification process assures there were no errors during the process.
If there are errors here are some things to do. Reformat the micro SD card. Download the Raspbian image again and use the new download. Run Balenaetcher again and use the new image file. Delete the older image file. If you still get errors then you may need to use a different MicroSD card.
At the end of the process, you will be informed the Flashing is complete. You will be prompted to Flash another. We don't need to Flash another. Quit the Etcher application. The Etcher application ejects the drive at the end of the process. Unplug the adapter and then plug it back in. The microSD card should appear on your list of devices. On Mac, it will appear on the desktop. On Windows, it will appear in the File Explorer. Look for the drive titled BOOT.
Chromebook
We used the Chromebook Recovery Tool when formatting the MicroSD card. This same tool will flash the Rasbpian OS onto the MicroSD card. Insert the card in one of the USB ports on the Chromebook. Open the Chromebook Recovery tool. Click the gear icon. Select the option to use a local image.
Go to the download folder. Select the Raspbian image. Click the open button.
In step two, you are prompted to select the external drive. Click the selector. Select the MicroSD card. Click the continue button. Click the Create Now button.
The process takes several minutes. At the end of the process, you are prompted to finish or to create another. Go ahead and quit. Leave the drive connected to the computer for the next step.
The SSH file
We are not going to connect a keyboard, mouse, or display to the Pi. This provides an added level of flexibility. We don't need to dedicate a display to a device that doesn't need one to monitor the weather.
Without a display, keyboard, or mouse we need a way to communicate with the Raspberry Pi. We will use a protocol called Secure Shell, SSH. This is how network servers are managed. The SSH protocol is not automatically available when the Raspberry Pi boots for the first time. We need to include one piece of information so it is enabled the first time the Raspberry Pi boots. This file must be on the card before the Raspberry Pi boots with it for the first time.
By the way, running the Pi without a display, keyboard, or mouse is described as running in Headless Mode.
Enable SSH using Mac
Open the terminal application. Type cd /Volumes and press the return key. This takes us to the Volumes directory. The MicroSD, like other drives, is seen as a volume.
Type ls and press the Return key. A list of the mounted volumes will display. Look for the boot volume.
Type cd boot and press the Return key. This places us inside the MicroSD card.
Type "ls" and the Return key to see a list of the files on the card. We are going to add one more file.
Type nano ssh and press the Return key. We are using a simple command-line word processor called nano. We have instructed the computer to use nano to create a file called ssh. The editor opens to begin editing the file.
We are not going to place anything in this file. Don't change anything in the file. Don't even press the space bar or return key. We need to create a blank file for Raspbian to enable the ssh protocol on the first boot and setup.
There are commands at the bottom of the nano application. Press the Control key and the letter "o" at the same time. This will save the file to the microSD card. The little arrow next to the letter is called a carrot and it represents the Control key.
The ssh file name appears for us to confirm we want to write the changes to the file. Press the Return key. The changes are updated and saved to the drive.
A message appears informing us we saved a file with "0 lines" of information. If you have any number other than zero please remove any spaces or hard returns. Press Control and "o" to save the updated file.
Press the Control key and the letter X to exit the nano editor. We are going to create another file. This file enables and configures the WiFi. This is an important step so we can work on the Pi in headless mode. Go over to the connecting to the Wifi lesson.
Enable SSH using Windows
Open the File Explorer and look for the MicroSD card. The card is named boot. The files and folders in the drive are part of the Raspbian OS.
Right-click anywhere inside the drive where you see the files. Select the option to create a new text document.
A plain text document is created. The file name is selected so we can replace it with our own.
Type ssh and press the Return key. The file does not need an extension.
SSH on Chromebook
We need to create a plain text file. Google Docs create and export plain text files. I prefer to use a specialized text editor for code. The editor is available from the Chrome Web Store. Open the Chrome Web store. Search for "text editor". We are going to use a very simple text editor. The editor is an extension. Click the "Add to Chrome" button. Authenticate the installation.
Look for the extension on your browser. Click on the extension.
The editor opens with a newly created document. Don't type anything into this document. Click the "Save as" button.
Click on the MicroSD card drive. It is labeled as External Drive.
Double click the boot partition.
The boot partition contains the system files for Raspbian. Don't delete, open, or modify any of the files.
The editor creates a random name for the file. Erase the name and type ssh. Don't include the quotation marks.
Make sure to erase the ".js" extension.
Click the Save button when the ssh file is properly renamed. We don't need this file open. Click the "x" to close the document. Leave the editor open for the next step.
Connecting to the WiFi
The first two versions of Raspberry Pi did not come with built-in wireless options. Wireless connections for the Internet and Bluetooth became available with version 3 and continue with version 4, which is the most current version at the time of the writing of these lessons.
The built-in wireless connectivity with Raspberry Pi 3 makes it much easier to use for this project. The first and second versions of the Raspberry Pi did not include wireless capability on the board. They need an extra device to connect to a wireless network. The extra device is a wireless adapter. The adapter connects to one of the USB ports.
I tested several wireless adapter options. I found that the Edimax EW-7811Un 150Mbps 11n Wi-Fi USB Adapter works well with my Raspberry Pi. I am using the Raspberry Pi Model B+ version 1.2. The adapter is less than $15 and well worth it for this project. This device is also one of the recommended devices on the Raspberry Pi website.
Connecting to a wireless network is almost a must to be able to place the temperature sensor in a location that will measure the temperatures we want. We want the sensors to be exposed to the outside. There are very few locations that have network drops outside the building. Wireless networks often extend beyond the building for several feet.
To connect with an existing network we need to provide some information on the microSD card during the first boot. This information is provided in a text file. This will be just like what we did with the SSH file. The SSH file didn't include any information.
The configuration file for our WiFi connection will contain information for connecting to a wireless network. We need to include this information so that the wireless is configured and established for us.
Mac WiFi configuration file
Open the Terminal application if it isn't already open. Type cd /Volumes/boot if you are not in the MicroSD card boot volume.
We are going to use nano again to create the file. Type nano wpa_supplicant.conf and press the Return key.
The file contains lots of information and instructions. It is often easier to copy and paste the code into the file. Copy and paste the code below into the nano editor.
country=US ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev update_config=1 network={ ssid="YOURSSID" scan_ssid=1 psk="YOURPASSWORD" key_mgmt=WPA-PSK }
The first line identifies your country. Change the line to match yours. The second line is used to control the wireless adapter through the wpa_supplicant configuration. The third line updates the configuration for the adapter. In the remaining lines, we provide the information for the wireless access network. The SSID or Service Set Identifier is the name of your wireless network.
Here are some basic instructions for navigating inside the nano editor. Use the up arrow on the keyboard to move the white square up. The white square is the cursor. Use the right arrow to move it to the end of the word YOURSSID. Make sure the cursor is highlighting the quotation mark. Use the delete key to erase YOURSSID. Type the name of your wireless network.
Press the down arrow key to go to the psk, passkey, line. Move the cursor to the end of YOURPASSWORD. Make sure the cursor is highlighting the quotation mark. Use the delete key to erase YOURPASSWORD and replace it with the password for your wireless network.
The password is case sensitive. Type it exactly or it will fail to connect. A failed connection means we need to manually configure the wifi. To do this we need to connect a display and keyboard to the P. It's messy. Please be careful.
Once the information for your network is entered we need to save the file to the microSD card. Press the Control key plus the letter "o". This will save the information to the file. We are prompted to confirm the name of the file. Press the Return key to continue.
Nano will confirm the saving of the file to the microSD card. Press Control plus the letter "x" to quit the nano editor. Type "ls" at the command prompt. Look for the SSH and wpa_supplicant.conf files we created.
Quit the terminal. Eject the microSD card. Place it to the side for the next lesson.
Windows WiFi configuration
Select the microSD card if it isn't already selected. We are going to create a text file like the one we created for SSH. Right-click in the boot drive and create a new text document.
Name the document "wpa_supplicant.conf". Press the Return key to save the new document name.
Open the file with Notepad. You might have to right-click and select open with Notepad.
We need to insert instructions in the document that will be run when the Raspberry Pi starts. Copy and paste the instructions below.
country=US ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev update_config=1 network={ ssid="YOURSSID" scan_ssid=1 psk="YOURPASSWORD" key_mgmt=WPA-PSK }
The first line identifies your country. Change this line to match yours. The second line is used to control the wireless adapter through the wpa_supplicant configuration. The third line updates the configuration. In the remaining lines, we provide the information for the wireless access network. The SSID or Service Set Identifier is the name of your wireless network.
Replace YOURSSID with the name of the wireless network you want to access. Make sure to leave the quotation marks.
Replace "YOURPASSWORD" with the password for the wireless network. Make sure to leave the quotation marks.
The password is case sensitive. Type it exactly or it will fail to connect. A failed connection means we need to manually configure the wifi. To do this we need to connect a display and keyboard to the P. It's messy. Please be careful.
Save the changes to the document and quit Notepad.
Both files need to be in the boot drive. They will be used by Raspbian to configure SSH and connect to the wireless network.
Chromebook configuration
The configuration steps on a Chromebook are the same as those used in Mac and Windows. We are just using a different text editor. Use the text editor extension we installed in the SSH lesson. It should still be open from that lesson. Copy and paste this code into the editor. If you can't copy and paste then make sure you type it correctly.
country=US ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev update_config=1 network={ ssid="YOURSSID" scan_ssid=1 psk="YOURPASSWORD" key_mgmt=WPA-PSK }
The first line identifies your country. Change the line to match yours. The second line is used to control the wireless adapter through the wpa_supplicant configuration. The third line updates the configuration for the adapter. In the remaining lines, we provide the information for the wireless access network. The SSID or Service Set Identifier is the name of your wireless network.
Replace YOURSSID with the name of the wireless network you want to access. Make sure to leave the quotation marks.
Replace "YOURPASSWORD" with the password for the wireless network. Make sure to leave the quotation marks.
The password is case sensitive. Type it exactly or it will fail to connect. A failed connection means we need to manually configure the wifi. To do this we need to connect a display and keyboard to the P. It's messy. Please be careful.
Click save as.
Change the name of the file to "wpa_supplicant.conf".
Select the external drive disclosure triangle. This reveals the volumes. Select the boot volume.
Click the save button in the text editor. Close the text editor. Eject the MicroSD card.
Assembling the Raspberry Pi
Before assembling the Raspberry Pi I like to insert the MicroSD card. It is much easier to insert the card when the Pi isn't surrounded by the case. Insert the MicroSD card into the slot on the Raspberry Pi. There is a mechanism inside that holds onto the card. I describe it like a pen that clicks. Push the card into the slot until you feel a slight click. You might need to use your fingernail.
There isn't much to assemble. The kit you ordered should have included a box for the Pi. Most Pi boxes come in three parts. The Pi itself goes onto the base. Place the Pi on the base for now. This will keep the electronic components from coming into contact with anything that might damage them. This is a good time to use the Static Strap if you purchased one.
The base and the Pi are enclosed in a protective case. The third piece is a cover. Don't place the cover on the Pi yet. We need to access the GPIO pins in a future lesson.
Weather Station Project Lesson 1
Weather station project using a Raspberry Pi. The Pi collects information from a temperature and humidity sensor. This lesson describes the project. The needed items for the project are outlined. The MicroSD card is formatted using the command line on MacOS and Windows 10. We also format the drives using Disk Utility, Windows formatting tools, and the Chromebook Recovery Utility. The drive is formatted for the creation of the Raspberry Pi boot image.
Introduction
This project is much longer than some of my other projects. It is also more technical than others. This project is something I always wanted to do in my classroom. It is also something I wanted to provide during professional development. At the time I lacked the resources and time to produce the product. The availability of inexpensive computes and components makes this project possible.
We will develop a basic weather station. The station will collect temperature and humidity information. The information will be published to a Google Sheet. The information in the form of data will be graphed with charts in Sheets. The charts will be published using Google Sheets and Google Sites. This provides live updated information from the temperature and humidity sensor.
The resources for this project are relatively inexpensive. You will need a Raspberry Pi to collect and publish the information. You will need a humidity and temperature sensor. Both sensors are in the module. You will also need a Google account.
We are using a basic computer called a Raspberry Pi. The Raspberry Pi is part of a kit. The temperature and humidity sensor is part of a separate kit. I recommend getting both kits. The kit that includes the sensor offers additional sensors and resources. I plan on creating and publishing a variety of lessons using these kits. Several kits provide similar resources. Here are the ones I recommend. I have links to the kits on Amazon. You don't have to purchase the kits from Amazon. The link is here to reference the actual product. The kits are available from their respective providers for education. Contact them for special pricing options. I have a summary of the kits here.
Raspberry Pi kit - The kit contains all you need to get started. Make sure the kit includes the power adapter, microSD card, microSD card adapter, and a case to enclose the Pi. I have links to these kits on Amazon and the Canakit websites. You don’t have to use the kits from these links. Purchase the Pi anywhere you want. Make sure it has the basic parts of the kit that I outlined above. The image below shows the components in the kit.
Raspberry Pi kit
Canakit website: Raspberry Pi 3+ Starter Kit
Amazon: Raspberry Pi 3 B+ Starter Kit
Arduino Kit - This kit contains another device known as a microcontroller. We are not going to use the microcontroller in this project. I will include it in future projects. The Arduino kit contains items we need for this project and future projects. The kit contains the temperature sensor we need. It also contains wires, resistors, and a breadboard needed for the project. The Arduino kit is usually less than half the price of a Raspberry Pi kit. I use the Starter kit by ELEGOO. I recommend the kit from one of the links below.
Elegoo Arduino Starter Kit
Elegoo: Elegoo Uno Super Project Starter Kit
Amazon: Elegoo Uno Super Project Starter Kit
Raspberry Pi version 1.xx and 2.xx users. If you have an older Raspberry Pi then use it instead of purchasing the latest version. These Pi devices did not include wireless capabilities. You will need wireless access to a network. Wireless access allows you to place the temperature sensor anywhere within the sphere of a wireless access point. You will need to purchase a wireless adapter for the Pi. I use and recommend the Edimax EW-7811Un 150Mbps 11n Wi-Fi USB Adapter. It is available from Amazon. It plugs into one of the USB ports on the Pi.
One item that is not on the list but important. You will need a computer and Internet access. You can use any brand of computer and operating system. I recommend a computer running Windows 10, Mac OS, Linux, or Chrome.
Here is another item I recommend. The sensors and the Raspberry Pi are sensitive to static electricity. There is a grounding strap that is used to reduce the risk of damaging the components. The anti-static wrist strap is available from Amazon. It costs a little over five dollars. A worthwhile investment to safeguard a $150 project.
Raspberry Pi Introduction
In this lesson, we are setting up a Raspberry Pi to run our weather station with a temperature and humidity sensor. I am using a Raspberry Pi version 1.2. I am doing this to make sure everything works if you happen to be using an older Pi. The latest Pi version at the time of this lesson is the Raspberry Pi version 4. This version is much faster than the original. All the versions can do the same things. The newer version is more expensive than the Pi 3. This is why I recommended it for our projects and provided the link for it.
Before we being, I want to go over what a Raspberry Pi is and why we are using it instead of a regular computer. A Raspberry Pi is a small computer. It is about a little larger than a credit card. It has a Processing Unit, processing memory, and storage. It does not come with a monitor, keyboard, or mouse. The lack of a keyboard and mouse may seem like a disadvantage. We will soon see they are not needed.
The processor on a Pi is not as fast as a desktop computer. It isn't even as fast as a basic smartphone. It has minimal RAM, Random Access Memory. The latest version has 1-gigabyte of RAM. In contrast to typical computers which include 8-gigabytes of RAM. Storage on the Pi depends on the size microSD card inserted into the slot. The Pi starter kit includes a 32 GB microSD card. Hum, I think that was the storage capacity of my first laptop in 1997.
Pi is small and underpowered in comparison to most modern computers. All that processing power, memory, and storage aren't needed for our projects. This device is not meant to replace your laptop or desktop. Its purpose is to help hobbyists and developers use an inexpensive platform to develop projects. It is often used to prototype much larger products.
The Raspberry Pi is a wonderful device to learn fundamental and advanced computer skills. With a Pi, we can build a web server to host a website. We can build a media center for audio and movies. We can attach electronics and sensors to monitor the environment. We can build on our home webcam. The list goes on and on.
The image of the Raspberry Pi on the page is from a Pi version 3. All the devices are very similar. There hasn't been much of a change physically from the first Pi. The original Pi included 26 GPIO pins. Version 1.2 and later included 40 pins. I'll explain GPIO pins later. Here is a basic overview.
It has four USB ports. These are used to connect devices like a keyboard, mouse, and USB drive.
It has one Ethernet port. This is used to connect the Pi to a network drop or router. Raspberry Pi 3 and 4 include WiFi and Bluetooth.
It has an HDMI port to connect to a display or television. An HDMI port transmits high-quality video and audio from the same port along one cable.
One Micro SD card slot. The micro SD card holds the operating system for the Pi. It is also the default storage location.
One Micro USB power input. The Micro USB port is used to supply power. The power can come from any source that provides 5-volts. This is typically a computer USB port, cell phone wall plug, or power adapter. Your kit came with a power adapter. Make sure to use this adapter. It provides the best performance and won't damaging your Pi.
One 3.5 mm 4-pole composite video and audio port. This is typically used for audio out or to connect a composite cable for devices without HDMI.
One CSI camera port. This port is used to connect an external camera. This camera is similar to the camera on a laptop.
One DSI display port. This port is used to connect to external LED displays. These displays are typically about the size of a small tablet. Some of them offer touch screen options.
40-pin GPIO connectors. This is the key to why we are using the Raspberry Pi. The acronym GPIO stands for General Purpose Input and Output. These pins will connect to our temperature and humidity sensor. They will supply power to the sensor and receive data from the sensor.
The large square chip in the middle is the Broadcom CPU. This is the brains of the Pi. The specifications for the Raspberry Pi 3 B+ are listed below.
Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ (B Plus) with 1.4GHz 64-bit quad-core ARMv8 CPU (BCM2837B0)
1 GB LPDDR2 SDRAM
Dual-Band 2.4GHz and 5GHz IEEE 802.11.b/g/n/ac Wireless LAN, Enhanced Ethernet Performance
Installing the Operating System
The Raspberry Pi should have been shipped with a Micro SD card. The typical size of this card is 16 or 32 Gigabytes. Either size is more than adequate for the project. The Micro SD card includes an SD adapter. This adapter is there to insert the SD adapter into a computer with an SD card reader. Many computers come with an SD card slot. The Raspberry Pi kit includes a Micro SD USB adapter. It looks like a small flash drive. The micro SD card plugs into the device. The device then plugs into one of your USB ports. This is a USB port on your computer. The microSD card connects to the microSD card slot on the Pi. We need a regular computer to set up the card for use on the Raspberry Pi.
The microSD card includes all the tools you need to get started with the Raspberry Pi. It includes NOOBS. NOOBS is someone new at something. Like a newbie. The tools on NOOBS are wonderful. Most of them are not needed for our project. The NOOBS installation includes the full Raspbian operating system. We are going to install a lite version of Raspbian. Here is the link to the official Raspbian page, raspbian.org. There is thorough documentation on the site if you are interested.
Formatting the microSD card
Doing this step is useful for one fundamental reason. You are going to need to know how to do this at some point. MicroSD cards can fail. Operating systems become corrupt. Systems often crash. Knowing how to reinstall the operating system is crucial in these situations.
I will walk you through the process in complete detail. As always, I assume you don’t have any experience with any of the technology we are using. Feel free to skip the steps you already know. Don’t fail to perform them because they are crucial to the successful operation of our project.
Insert the micro SD card into the adapter that came with your kit. Insert the SD card adapter into your computer. This next step is not necessary but I like to go over the process. We are going to format the micro SD card. I like to do this so you know how to format the card if it becomes necessary. The card is in constant use and it doesn't take much to corrupt the contents of the card. It has happened to me on more than one occasion. Formatting assures we are installing the operating system on a reliable card. The process for formatting the card depends on your computer's operating system. I will go over the process using Windows 10, macOS, and Google Chrome for Chromebook.
The MicroSD card is formatted using the MS-DOS FAT 32 format. FAT stands for File Allocation Table. MS-DOS stands for MicroSoft Disk Operating System.
The terminal
This is the part that might scare some people. We are going to use the command line for almost all of the remaining lessons. With the command line, we don't use the mouse. We don't have a graphical user interface. The terminal is an application that provides access to the command line. The command line is where we enter instructions with the keyboard. The mouse isn't used so there is nothing to click. The command-line instructions are all available in this lesson. You can copy and paste them to avoid making mistakes. I encourage you to type them out on your own.
I will cover how to format drives using the regular formatting tools in Windows and macOS. This is for those not sure about jumping into the command line right away.
Formatting on Mac
To use the command line on Mac we need to open the Terminal application. The application is in the Utilities folder. The Utilities folder is inside the Applications folder. Open the Utilities folder and look for the Terminal application. Launch the Terminal. The Utilities folder contains the Disk Utility too. We will use this later to format the same drive. This is for those of you unwilling to try the command line yet.
A window opens with some text. The name of your user account on the computer appears to the left of the command prompt. The command prompt is the percent symbol. The blinking square next to the prompt is the cursor. The tilde next to the percent symbol indicates you are in the account’s home directory.
Okay, let's issue a terminal command. We want a list of the contents of our home directory. Type 'ls' and press the Return key. You will get a list of the folders and files in the home directory. Some of the names you might recognize as folders. These include the Desktop, Documents, and Movies folders. Folders are directories on a computer.
Type 'ls -l' and press the Return key. The "-l" after the "ls" command is an option. The "-l" instructs the list command to provide additional information. It shows file or directory, size, modified date and time among other things.
There is a pattern of letters on the left side of the list. The first letter indicates if the item is a directory or folder. All the items in this list are directories except for humidity.py. This is a file. Type "clear" and press Return.
Clear erases the contents of the terminal window. How’s it going. Not hard, Right?!
It is important to properly identify the micro SD card. I recommend you disconnect and remove any non-essential storage devices from your computer for this step. This includes any external hard drives. I have accidentally formatted external drives myself. Do yourself a favor. Disconnect any external drive.
Type diskutil list and press the return key.
A list of any attached drives will be generated. The micro SD card we inserted will be shown with its storage capacity. The card I am using is a 16 GB card. It appears on the list as 15.9 GB. The card will have one of two possible names. It might be titled BOOT or untitled. The card is formatted using the FAT32 format. The computer drive on Mac is typically formatted using the APFS format. These are additional clues to identify the card on your machine.
There is some important information related to the micro SD card that we need before formatting. The device has what is called an identity. The identity number is shown on the left. The device identity for my card is “disk2”. The device identity on your drive might be different. Make a note of the disk identity and jot it down somewhere. You are going to need is soon.
The command instructions for formatting our micro SD card are as follows, “diskutil eraseDisk FAT32 BOOT /dev/disk2”. Press the Return key to execute the command. Don’t include the quotation marks if you are copying and pasting. Replace my disk identity with yours.
Here is what the instructions represent. We call the diskutil application to erase a disk. The disk will be formatted with the FAT32 file system. The disk name will be BOOT. The disk name needs to be in All Caps when using the FAT32 file system. The location of the disk to be formatted is in the dev directory. The identifier of the drive is disk2.
A formatting progress bar appears. The formatting process doesn’t take long. It usually takes a few seconds. If you didn’t see the formatting progress bar then go back and check the commands. You might have made a mistake in the spelling. You might have omitted one of the instructions. Always check your instructions before pressing the Return key.
When the process is complete you will see some messages. One of the lines will read "Finished erase on disk". The disk identifier will match your micros SD card.
The formatted disk will not appear on your desktop. The disk is unmounted after formatting. This means the disk volume is ejected. To see the drive you will need to unplug the drive and plug it back into the computer. Unplug the drive and put it aside for the next lesson.
Formatting on Windows
Formatting external devices on Windows has changed over the years as the Windows operating system evolves. These instructions cover Windows 10. Insert the micro SD card and adapter into one of the USB ports on your computer. Click in the search box on the Task Bar and type CMD for Command.
The Command option takes us into the command prompt. We want to run the Command Prompt as an administrator. Click the Run as administrator option.
You might be asked to allow the Command Prompt to make changes on the device. Click the Yes button.
A Command Prompt window opens. This looks similar to the Terminal on MacOS.
Type the command diskpart and press the Return key.
Diskpart is a command tool used to manage drives on the computer. The Windows Command Prompt is replaced by the DISKPART prompt.
Type list volume and press the Return key. Drive volumes attached to the computer will be listed. I recommend you remove or disconnect any external drives. This reduces the chance that you might select the wrong drive.
Looking at the list we see several volumes. Each volume has a letter and label. There is a column with the file system used for each drive. We want to look for a drive that has the FAT32 file system. Windows uses the NTFS file system for its main drive and larger drives. We see that the drive with the FAT32 file system is removable. The size column shows that the drive is close to matching the size of our micro SD card. My card has a storage capacity of 16GB. The column shows 14GB. The sizes of the other drives are in no way close to matching this size. The micro SD card on my computer is assigned Volume 4. Make a note of the volume number for your SD card. Type select volume followed by the volume number for your micro SD card.
Look for a message confirming you selected the appropriate volume.
Type the command below and press Return. The card is formatted with the FAT32 file system and labeled BOOT.
Diskpart> format fs=FAT32 label=“BOOT” quick
A completed message appears at the end of the process. Remove the adapter and microSD card. Set it aside for the next lesson.
Formatting with Disk Utility
Eject and remove any external storage devices except the microSD card. Open the applications folder and then the utilities folder. Look for the Disk Utility application. Open the application. Look for an external drive. The drive will probably be titled BOOT. Click once on the drive.
Here are ways to verify you have the correct drive selected. The drive is formatted as MS-DOS FAT32. Verify the storage capacity with the card you are using. The kit includes a 32GB SD card.
Click the Erase button. Click the format selector. Select MS-DOS (FAT). Click the Erase button.
The erase process doesn’t take long at all. Click the Done button to finish. Eject the SD card and put it away for the next lesson.
Formatting on Windows
Insert the SD card into one of the USB ports on your computer. Open the File Explorer.
Look for the drive with the name BOOT. Click on the drive.
Click the Drive Tools tab. Select Format.
Click the File system selector. Chose the FAT32 format. Click the Start button.
Eject the SD card and put it away until the next lesson.
Formatting on Chromebook
The Chromebook is different from your typical computer that runs and OS like Mac or Windows. The Chromebook runs a version of Linux. Linux is a free open-source operating system. The operating system is based on Chromium OS. The MicroSD card is preinstalled with another Linux version based on Debian. This matters when we need to format the microSD card.
Typical drives like flash drives and microSD cards are easy to format. The card that came with your kit comes with Linux preinstalled. The card is specially formatted and partitioned into volumes. You will see what I mean in a moment. To format the drive we will use a recovery tool. This tool will be used later to create our boot media for the Raspberry Pi.
The Chromebook recovery tool is available in the Google Chrome store. Go to the Web Store by clicking the icon.
Search for the Chromebook recovery utility.
Add the utility by clicking the Add to Chrome button. Confirm the installation when you receive the message.
Find the utility in the Chromebook launcher and open it. Insert the microSD card with the USB adapter. Click the gear icon in the recovery utility. Select the option to erase recovery media.
Select the microSD card when prompted to select the recovery media. The SD card should be the only device that appears. Click the Continue button.
Click the Erase button to confirm. The process doesn’t take long. A second or two. A message appears to confirm the process is complete. Click the done button. Close the utility. Unplug the MicroSD card and set it aside for the next lesson.
There are times when an error message appears. Try the reformat process again if this happens. If it continues to happen you will need to use a different microSD card.
Why the Recovery Utility?
Normally we don't need the recovery utility to format an external drive. It made sense in this case. The formatting of the microSD card that came with your kit is different. Let's take a look. The formatting of external drives takes place in the Files utility.
The connected microSD card looks like this when inserted.
It typically looks like this.
The external drive in our media is partitioned into two volumes. Google does not have an option to configure partitions. We want to remove the partitions and have one for our system. The recovery utility allows us to format the device and remove the partitions that exist.
Enhanced Dice App Lesson 5
In this fifth lesson, we are going to add to our exiting animation. The dice are currently rotating. Dice are often thrown in the real world. I want to simulate what the dice might look like if they are thrown and are flying toward the stage.
Enhanced Dice App Lesson 5 of 5
In this fifth lesson, we are going to add to our exiting animation. The dice are currently rotating. Dice are often thrown in the real world. I want to simulate what the dice might look like if they are thrown and are flying toward the stage. In this animation, the dice will begin as smaller versions. This is intended to simulate that they are being thrown from a distance. The dice will gradually get larger until they come to rest at their original size.
Changing the dice size from small to large creates perspective. It creates a sense of motion. The dice will reduce in size when the button is pressed. The dice will increase in size as they roll and go through each loop. We need some math to help us do this.
The math is easy. The size of the sprites is set to 75 percent. The loop is set to iterate 10 times. We are going to create variables that will render the correct animation regardless of the values. The animation will work even if we change the number of iterations or the size of the dice.
Select the "Die1" sprite. Go to the Looks section and place the "change size by" code on the canvas. Don't attach it to the main code yet. We want to change the size of the image by a percentage. We need to calculate this percentage and place it in a variable. The code will receive the percentage from the variable.
Go to the variables section. Create a variable. Set the variable name to "Dice 1 size".
Place the variable into the "change size by…" parameter.
Place the code at the beginning of the main code string. The code is at the beginning because we want the sprite to resize before other effects are applied.
Select the "Die2" sprite. Place the "change size by" code at the beginning. Create another variable. Set the variable name to "Dice 2 size". Add the variable to the size parameter.
Select the "rollButton" sprite. Place the set code block from the variables section onto the canvas. Don't attach it to the main code yet. Change the set option to "Dice 1 size".
Place the divisor operator into the set parameter.
It is always a good idea to create variables to pass values into parameters. Create two variables. Set one of the variable names to "diceSize" and the other to "diceTurns". Place the "diceSize" variable into the numerator parameter. Place the "diceTurns" into the denominator parameter.
I chose these variable names to make it easier to understand what is going on here. Read the code block like a sentence. Set the dice 1 size to the dice size divided by the dice turns. Place this code at the beginning of the repeat loop.
Place another set code block in the loop. Place the code below the other set code. Change the set to "Dice to size". Add the operator to divide the dice size by the dice turns.
We need to set the values for our variables before running the program. This is called initializing the variables. Place two set variable code blocks before the repeat loop. Set the dice size to 75-percent. Set the dice turns to 10.
The repeat parameter in the loop needs to get its value from the variable we created. Place the "diceTurns" variable in the repeats parameter.
We are getting closer to the finish. The dice will spin and change size each time through the loop. The size depends on the denominator. The denominator needs to get smaller each time. This is so the size of the sprite gets larger each time. An easy way to look at this is to look at a table with the values from each pass in the loop.
In the table below we see that the initial image size is divided by 10. The size becomes 7.5 percent of the original size. The second time through the loop, the size is divided by 9. The size is now 8.3 percent. Each time through the loop the size gets a little larger as the denominator gets smaller. I think this a great way to show the relationship between denominators and numerators.
To change the size we need to change the "diceTurns" value. The loop has an internal counter. We need to create and use a counter of our own. Place a change code block from the variables section before the end of the loop. Change the variable to "diceTurns". The parameter is set to change the variable by 1. This will add one to the current "diceTurns" value. We want to decrease the value. Change the positive one to a negative one.
The code for our button is done. We need to update one code block in our sprites for this to work properly.
Go to sprite "Die1". Pull away the code at "start sound".
Remove the "change size by" code. Replace it with "set size to". Reconnect the code.
Place the "Dice 1 size" variable in the "set size to" parameter.
At the end of the loop, we will have an image of the dice that is the same as when we started. It is still good practice to set the initial size of our object at the beginning. Place a set size code block onto the reset code. Change the parameter to 75 percent. I entered a number into this variable. Is this the proper way to do this?
If you said no, then you are right. We need to use a variable in place of the 75 percent we entered. Replace the value 75 with the variable Dice 1 size.
Repeat the process with the "Die2" sprite. Make sure to use the "Dice 2 size" variable. Click the Roll button to run the app. The sprites will reduce in size at the beginning. They will get larger as they go through the loop. They will return to their original size at the end of the loop. If something doesn't go well then you need to go back and check the code. Review the images in my instructions.
There are information boxes on the stage along with the sprites. The information boxes show the values in the variables. Use this information to help troubleshoot any bugs in the app. Remove the information boxes when the app is working fine. To remove the boxes you need to remove the checkmark from each variable.
The link to my dice app is available below. Make a copy and use it to build on for your app.
Enhanced Dice App Lesson 4
This is the fourth lesson in a five-part lesson project. In this lesson, we will add some visual effects to the animation. There are some effects for images that distort and colorize sprites. You will learn how to apply any of the effects to the sprite to add some visual appeal.
Enhanced Dice App Lesson 4 of 5
Visual effects
This is the fourth lesson in a five-part lesson project. In this lesson, we will add some visual effects to the animation. There are some effects for images that distort and colorize sprites. You will learn how to apply any of the effects to the sprite to add some visual appeal.
Anything that affects the appearance of a sprite needs to be added to the sprite. Select the “Die1” sprite. Go to the Looks section. Place a “set effect…to…” code block at the end of the code. The block parameter is set to change the color of the sprite. The effect value is set to zero. A value of zero will not add any effect.
Click the effects selector. Select the fisheye effect.
Change the effect to 20. The number represents a percentage. There is nothing magical about this number. I chose it because I wanted to get a hint of what the effect would produce on the image. Click the Roll button. Observe what happens to the image.
We applied the effect to one sprite for now. Once we settle on an effect it will be applied to the other sprite. I like this effect because it is subtle. Chose an effect for your Sprite.
Before applying the effect to the other sprite we need to reset the effect for the next roll. Keeping the effect after the dice finishes rolling doesn’t look correct. Place the “clear graphic effects” code under the reset code. Add the same effect code to the other sprite.
Return to the “rollButton” sprite. We need to call the reset message at the end of the animation. The reset is currently applied to the beginning. The images need to be reset after the animation and effects is complete. Place another broadcast reset code after the loop. Click the Roll button.
Our app is finished for now. I hope you learned several things to make your app more interesting to use. Before we finish I want to include one more step. I want to add more animation. I want to simulate dice flying into view. To do this we need to use some math and a little animation. That will be the topic of the next lesson.
Enhanced Dice App Lesson 3
In this lesson, we add sound. The sound will simulate dice clicking against one another or onto a surface. We will use one of the sound effects available in the Scratch development environment.
Enhanced Dice App Lesson 3 of 5
Adding sound
This is the third lesson in our dice app project. The first lesson rearranged the code from a lesson where we built a basic dice app. The second lesson added basic animation. In this lesson, we add sound. The sound will simulate dice clicking against one another or onto a surface. We will use one of the sound effects available in the Scratch development environment.
Dice bump into each other and onto surfaces. When they do they make a clicking sound. We are going to add that clicking sound here. Select the “Die1” sprite. We are going to assign the sound to the sprites. The sound will be the property of each sprite. We will use the individual properties to have a distinctive sound for each sprite. Click the Sounds tab.
Go to the insert sound options and select choose sound. Scratch has a library of sounds for us to use.
There are many sounds to sample. I will be using an effect. Click the Effects button.
Find the Finger Snap effect and click on it.
The effect is represented as an image. This image is a sound wave. There are tools below the wave to modify the sound. Click the play button to listen to the effect. I want the snap to sound more like something tapping. Click the Faster button once. Click the play button to listen to the sound. The sound has a higher pitch. Note how the shape of the sound wave changed when we increased the pitch.
Rename the sound to Dice Click. Click the Code tab to return to our sprite.
Go to the Sound section. Find the “start sound…” code. Attach the code to the beginning of the code. The sound Dice Click should be selected for us.
We need to add a similar sound to the “Die2” sprite. Go to the “Die2” sprite and add the “start sound” code. Sounds are associated with each sprite only. The effect we chose here is not available for the “Die2” sprite. The Dice Click effect option does not appear when we insert the code.
Repeat the steps from above to create the effect for this sprite. Change the name to Dice 2 Click. Don’t change the pitch. Return to the code and select the effect. Click the Roll button to test the program. That sounds great!
We need to change something. The dice are spinning very fast and the sound doesn’t sound much like clicks. This is because the event is happening too fast. We need to slow things down.
Go to the “rollButton” sprite. Insert a wait code block. The code is found in the Control section. Place the code at the beginning of the loop. Click the Roll button. The animation and sound have slowed down too much. One second is a long time when we are referring to computer coding.
Reduce the wait time to half a second. Enter .5 into the wait parameter. Click the Roll button. This is faster but I think it should be faster.
Reduce the wait time. Half of half a second is .25 or a quarter of a second. Change the wait time and click the Roll button. That sounds better to me.
The wait time is measured in seconds. Typical code uses milliseconds. That is thousands of a second. A second has one-thousand milliseconds. We need to use fractional or decimal equivalents. This is why I halved the wait times.
The dice are spinning at the same rate. They are synced. Tossed dice are rarely synced. We need to add some delay to one of the dice to have them offset. Insert wait code before the second dice set code. Change the wait time to match the other wait time. Click the Roll button. Change the wait time of one to increase the offset. Adding wait time slows the animation.
The animation and sound for the app are done. I would like to make the animation look more interesting. That will be the topic of the next lesson.
Enhanced Dice App Lesson 2
In this lesson, we continue from last week's lesson. Last week we organized our code in preparation for a larger project. We are moving over to the sprites and adding basic animation.
Enhanced Dice App Lesson 2 of 5
Dice animation
In this lesson, we continue from last week's lesson. Last week we organized our code in preparation for a larger project. We are moving over to our sprites and adding basic animation. The dice will spin and change face values as they spin. We will return to the button code and include a variable to set the rotation angle.
Click on the "Die1" sprite. Go to the Motion section. Attach the turn clockwise code block to our code. Repeat the process with the "Die2" sprite. Choose the counterclockwise code.
Click the Roll button to test the code. The dice images spin. This works fine but they land at awkward angles. The dice rotate fifteen degrees during each loop. They go through the loop ten times. The dice rotate a total of 150 degrees. For the dice to land flat they need to land at a 90-degree angle. We can choose multiples of 90-degree angles. The possible angles include 90, 180, 270, and 360. If we leave the number of loops set to ten, we can set the angle of each rotation to 9, 18, 27, or 36. We can try each of these to find one that we think works well.
The values in our turns are manually entered into each dice sprite. This isn't efficient or convenient. We need to create a variable that will pass a value to each turn without having to constantly go and change the value in each sprite. Go to the variables section. Create a new variable. Name the variable rotation.
Place the rotation variable into the "Die1" and "Die2" sprites code.
Go to the "rollButton" sprite. Place the set variable block in the loop below the last code. Change the variable to "rotation".
Set the rotation parameter to 18. This will rotate the dice and they should land flat after rotating 180 degrees. Click the Roll button.
The dice spin but they still land at the same awkward angle. The code is working fine. They are at this angle from the previous code we used. We need to make sure to reset the rotation of the blocks before running the program. This is part of what we do with all programs. We set the default values.
Properties for sprites need to be associated with each sprite. To reset each dice sprite we need to insert reset instructions into each. Click the "Die1" sprite. Place a "when I receive…" code on the stage. This code is in the Events section. The code is not attached to our existing code. It stands on its own.
Click the message selector and create a new message. Set the message name to "reset". Select this message in the message received event.
Attach a "point in direction…" code block to the reset message received. The "point in direction" code is in the Motion section. The direction is set to 90-degrees. Click on the "Die2" sprite and repeat the process. You don't have to create a separate variable for the message. Use the same variable.
Go to the "rollButton" sprite. Place a broadcast code block before the repeat code. Change the message to reset. Click the Roll button. The dice will spin and display a random face value. The dice will land at a 90-degree angle.
That’s it for lesson two. In the next lesson we will add sound to the dice app.
Enhanced Dice App Lesson 1
In this lesson, we are adding a button to trigger the animation. We are also organizing the code to develop a more sophisticated app. Our Code should always be as simple as it can be.
Enhanced Dice App Lesson 1 of 5
Button code
In this lesson, we are adding a button to trigger the animation. We are also organizing the code to develop a more sophisticated app. Our Code should always be as simple as it can be. This reduces the number of errors possible and makes debugging our code much easier. The more complex the app the more we need to keep our code simple and organized. That is part of what we will do here.
We are going to build on our existing code. We are going to make a copy of the app. This allows us to keep the original and build on the existing code and graphics. Go over to scratch at https://scratch.mit.edu. Log into your account. Click the folder icon to access your projects.
Find the app you created. Click the “See inside” button to open the app in edit mode.
Click File and select the option to save a copy.
If you didn’t create the first app, I encourage you to return and create the app. It will help you understand what we will do here. You can jump right into this lesson by making a copy of my app. Use the link below to get a copy. Update the file name for the copy. Replace the word copy with number 2.
https://scratch.mit.edu/projects/341906863
The loop
The dice faces change when we click the flag button. A random number is generated and the dice faces change to the corresponding number. To animate the dice we place our code into a loop. The loop will run the random number generator and change the dice face a specific number of times. Pull away the first code block from the flag event.
Go to the Control section and find the repeat code block. The repeat block is commonly referred to as a loop. I will refer to is as a loop too.
Drag the repeat code block toward the top of the first code block. Look for a shadow of the repeat block to appear around the code. Release the code block.
The loop will repeat the code we created. The loop has one parameter. The parameter is used to tell the loop how many times to repeat the instructions. The parameter is automatically set to 10. We will use this value.
Attach the repeat block to the flag event. Click the flag event. The set code is calling the dice sprite on the left. The die will change face values ten times. The faces change fast. It’s almost difficult to see. The one on the right will run once. The code we are modifying is associated with the left dice sprite only.
There is an acronym in programming, DRY. Don’t Repeat Yourself or don’t repeat patterns. Our code is a pattern of instructions. If we were to repeat the instructions for the dice on the right we would be repeating a pattern. We repeated the code in our first app. The app is simple so repetition isn’t anything to worry about. In larger programs, we need to reduce or eliminate repletion. The goal of programming is to make things easier and simple. Repeating a process or pattern is complex and inefficient. Repeating patterns makes it difficult to fix mistakes or find errors.
App button
To avoid repetition we will assign the code to one sprite. We will create a separate sprite to send instructions to the dice faces. This sprite will be a button. We will create this button right inside Scratch. Go to the Sprite section. Click the add Sprite button. Select the brush icon.
A paint application opens. Click the rectangle tool.
Draw a rectangle in the drawing canvas.
Click the shape fill selector. Move the sliders to change the button color. Chose a color you like. Choose a dark color.
Click the text tool.
Click once on the drawing canvas to insert a text box. The text box does not need to be inside the rectangle we just drew. Type the word ROLL.
Select the text in the text box. Click the color fill option in the button bar.
Move the saturation slider to the left. This will remove the color from the text. The text will be white. White contrasts well with our button color. Contrasting colors are easier to read on a screen.
Move the text box and center it inside the rectangle.
Use the corner handles to resize the text box.
Position the resized text box in the center of the rectangle.
The sprite button we created appears on the stage with the dice sprites.
Move the images on the stage. Position the button and dice images so the dice images are above the button. Center the button below the dice sprites.
Coping code to other sprites
Click the Code tab to return to the coding canvas.
Select the “Die1” sprite.
We are going to copy our existing code blocks and attach them to the button. Click the flag event code block and drag the code blocks to the sprites section. Drag the code over the button sprite and release.
The code blocks will snap back to the canvas. It doesn’t look like it, but we just copied the code to the button sprite. Click the button sprite to see the code blocks. If you don’t see the code blocks in the button sprite then try copying them again.
Return to the “Die1” sprite. We don’t need the code attached to this sprite. Click and drag the code blocks out of the canvas and into the code blocks panel. Click the “Die2” sprite and remove the code blocks. Return to the button sprite.
Go to the sprite name field. Change the name of the sprite to “rollButton”. We combined two words without spaces. This is a common way to create names and variables. This format is known as Camel Case. It is called Camel Case because the shape of the lower and upper case letters resembles the shape of a camel. Each capital letter is like the hump on a camel. We don’t include spaces to avoid errors when typing the name.
Calling events on sprites
The code block will cycle through the die costumes ten times. The costumes on the die won’t change until we send a message to the die sprite to change costume. Go to the Events section. Look for the broadcast code block. Place it below the set code block in the loop. This code sends a generic message to any code block that is listening. It is better to have a message name that describes what the message wants or does. Remove the switch to costume code.
Click the broadcast message selector. Click the New Message option.
Type “changeCostumeOne” in the message name field. Click the OK button.
These two code blocks will change the face for the first dice. We need to repeat the process for the second dice. Right-click on the set code block. Select the Duplicate option.
The duplicate code attaches itself to the pointer. Attach the code to the bottom of the existing code.
Change the duplicate set code block parameters. Change “die 1 face” to “die 2 face”. Change “die1costume” to “die2costume”.
Click the broadcast selector from the duplicate broadcast code. Create a new message.
Title the new message “changeCostumeTwo”.
Our basic loop code is setup.
Dice sprite listeners
We need to add listeners to each dice sprite. Click on “Die1” sprite. The “Die1” sprite canvas should be blank. Go to the Events section. Place the “When I receive…” code on the canvas. This code listens for a message.
Click the message selector and choose “changeCostumeOne”.
Go to the Looks section. Place the “switch costume to …” code below the message code. The costume selector lists all the sprite costumes. We need to change to the costume selected by the random number generator. The costume information is stored in the “die 1 face” variable.
Go to the variables section. Place the “die 1 face” variable into the costume selector parameter.
Click on the “Die2” sprite. Follow the same steps. Add the message code to the canvas. Listen to the “changeCostumeTwo” message. Attach the switch code to the message code. Use the “die 2 face” variable for the costume parameter.
Button sprite event
Go to the button sprite. The code in the sprite has the flag button event code at the beginning. The purpose of a button is to have someone press the button instead of the flag. Drag the repeat code away from the flag event.
Remove the flag event by dragging it to the code panel. Go to the Events section. Place the “when this sprite clicked” code on the canvas and attach it to the repeat code. Click the button sprite on the stage. The dice faces will change as they receive messages from the button sprite code.
Now that our code is organized it’s time to animate our dice. That is in the next lesson.
Dice App Graphics
In last week’s lesson, Creating a Dice Game with Scratch, we created a dice app in Scratch. In that lesson, I provided the dice images for the app. I thought it would be a good idea to show you how I created those images. I am using a free online illustration app.
Introduction
In last week’s lesson, Creating a Dice Game with Scratch, we created a dice app in Scratch. In that lesson, I provided the dice images for the app. I thought it would be a good idea to show you how I created those images. I am using a free online illustration app. The app is available at https://vectr.com.
The app doesn’t require an account to use. This is good news if your students don’t have Google accounts or are below the age of thirteen. If students do have a Google account then I encourage them to use it. Creating an account allows us to save our project online. Go over to https://vectr.com/login and create your free account. Click the Sign-up button to create an account with one of these services. You can use a different email if you don’t have Facebook, Twitter, or Google.
Dice project Graphics
We need a file to create and store our project. Click the Create File button.
A drawing canvas is opened for our project. There are several tools available to make our project. We will explore some of them while creating the project. Go over to the right side of the canvas. There are five icons. The first three are grouped. Click the center button on the three that are grouped.
The box below the button is where we provide a name for the project. Change the current name of untitled to “Dice Face Images”.
A button appears once we provide a name. Click the button to save the project with the new file name. Leave the other options alone. Make sure the measurement is set to Pixels.
Click on the first button on the left. This opens snapping and grid options.
Select the grid option.
A grid appears on the canvas. This gird will help us in the design of our project.
There is a Shape bar on the left side of the canvas. Look for the ellipse shape. Click the shape to select it. We are beginning the design with the dice circles.
Click and drag a circle shape on the canvas. You will notice that the shape is either a circle or an ellipse. It all depends on how you are dragging the arrow as you draw it out. There is a trick to keep the shape in the form of a circle. Press and hold the shift key with our other hand while dragging the circle.
Your circle should look something like this. Don’t worry if it doesn’t match exactly. We will take care of this later. It’s also okay if the shape isn’t an exact circle. We will take care of this too. The color of your shape is different each time. Don’t worry about the color for now.
Release the shape. Make sure it is still selected.
There is a properties box on the lower right side of the canvas. The box contains information about the width and height of the shape. The width and height of my shape are close but not exact.
There is an icon between the width and height measurements. It looks like a chain link. The measurements are linked to each other. Click the icon to break the link.
The link icon will disappear. Change the size for the width and height. Change each measurement to 100px.
The image on our canvas is now a nice circle.
We need more circles for our dice faces. We will make a copy of this shape. Right-click on the shape. Select the duplicate option.
A duplicate appears and overlaps our original shape. Click and drag the shape to one side of the original.
Lines appear around the shape as we move it on the canvas. These are guides. They help us align the object on the canvas. Move the circle so it is parallel to the other.
We want to use the guides to make sure the shapes are parallel to each other. Click and drag the original shape until you see guides appear all around the shape. These guides are aligned with the major grid lines. Major grid lines are darker. Minor gridlines are between major grid lines. Release the shape.
Move the other shape. Use the guides to place the shape within the major grid lines. Make sure the shapes are parallel.
We want to space the shapes so they are even across the dice face. Drag the second shape so that the guides fall on major gridlines. Space them so there is one major square between them.
Right-click and duplicate the second circle.
Place the third circle in line with the other two. Space it so there is a major square space between them. These three circles will create the dice face that represents the number six.
Duplicate each circle and place it below each of the three circles. Leave one major square between them. Use the guides to help align the shapes.
Each set of circles represents the numbers on the dice faces. We need a shape to represent the dice itself. Go to the shape bar and select the rounded rectangle shape.
Draw a small rectangle shape above the left circle. Before drawing the full shape we need to know what size to make the shape.
To figure this out we need to look at the size of the circle shapes. Each circle shape is 100 pixels in diameter. There are three circles across so we have 300 pixels in circles. There is a space between each circle. This space is one major square.
Look closer at the circle. The diameter takes up two of these squares. If two squares are 100 pixels then each square is 50 pixels. There are two spaces between each circle. This adds another 100 pixels. We are now up to 400 pixels. We will begin with this value.
Make sure the rounded rectangle is still selected. Go to the properties box. Make sure the link icon is not showing. Change the width to 400px. Leave the height alone for now.
Click and drag the rounded rectangle shape so it is above the circles and centered. Use the guides to help you align the shape. The shape matches the circles from left to right.
This doesn’t leave any space to the left or right. A dice has space on either side of the dots. We need to add some space. We will add 50 pixels on either side. This the spacing consistent.
Go to the property box and change the width of the rounded rectangle to 500px.
Return to the shape on the canvas and move it so the center matches the center of the circles.
Return to the properties for the rectangle. Change the height to 500px.
The rounded rectangle is done but it covers the circles.
Each shape is placed on a layer. Each layer is like a piece of transparent paper. The layers are listed in the layers panel on the left. The rounded rectangle is at the topmost layer. The rectangle layer needs to be placed below the ellipse layers.
Click and drag the layer below the last ellipse layer. A purple line shows where the layer will be placed.
All the circles are visible. We need to space the bottom three circles. We want them closer to the bottom of the rounded rectangle.
Click and drag one of the circles. Place it so the spacing from the edge matches the circles on top. The circle needs to be 50px from the bottom edge. Use the guides to align it with the circle above.
Repeat the process with the other circles.
Colors
Let’s change the colors of our dice face. Click on the rectangle shape. Every shape has a background and border color. The background color for my shape is light blue. Click the color to open the color picker.
Move the color slider on the right to one of your favorite colors. The gradient on the left is used to select the shade for the color. For example, move the slider toward blue. The shape background color changes to match.
Move the dot in the gradient to make the color darker or lighter. Move the slider and the dot to find a color you like for the dice background.
Change the color of the circles using the same method. Click on a circle and choose a contrasting color. For example, if you chose a dark color for the dice background you should choose a light color for the dice circles. I chose a light yellow for my circle.
We need to use this color for the other circles. The color picker keeps track of the colors we use. The colors are represented by a code. The code is shown in the box below the color selector. The color code begins with the “#” symbol.
Click on another circle. We want the circle to be filled with the same color. Click the background color button. Click the eyedropper tool next to the color code box.
The arrow for the mouse is replaced with a color picker. Move the color picker over the color of the previous circle. Click to select the color.
The color of the circle changes to the color you selected. Repeat the process with the remaining circles. Remember to select the circle that needs a color first. Choose the color you want with the color picker.
You are finished with the first face of our dice image set. The creation of the rest of the images is much easier.
Adding pages
Each image is constructed from shape layers. The image layers are part of a page. Our first dice image is on one page. Click pages to switch to the pages section.
We are going to use our first image as the basis for the remaining images. This will save time. Click the duplicate icon. The icon is below the image page preview.
The page is duplicated and selected for us. A light border appears around selected pages.
Go tot he image for this page and click the top center circle. Press the delete key on your keyboard to remove the circle from the image. You can also right-click the shape and select delete.
Select the center circle on the bottom and drag it up toward the center.
Use the guides to help you align the circle.
We have our face for the number five dice face.
Click the duplicate button for the second page.
Click the center circle and press the delete key on your keyboard. We now have the dice face for the number four. Duplicate this page.
Delete one of the corner circles. Move the other circle to the center of the shape. We now have the face for the number three. Duplicate the page.
Remove the center circle. Duplicate the page.
Remove one of the corner circles. Move the remaining circle to the center.
Downloading the images
We are done with all the dice face images. The next step is to download the images. The images will be uploaded to your own Scratch Dice App. We need to download each image separately. The last image is currently selected. This image represents the number one.
Return to the panel on the right side of the canvas. Click the export button.
The image appears in a preview area. The grid background has disappeared. The grid is not saved as part of the image.
The preview configuration panel has several options. We are exporting the selected page. The image is set to be exported using the SVG, Scalable Vector Graphic format. The size of the shape is 640 by 640 pixels. There is a link to this image by we won’t be using that here. There is a download and print button.
The image is set to be exported as an SVG. This is a very good format to use. This format is hard for other programs to use. I like to change the format to one that is more universal. Click the image format selector and choose PNG, Portable Network Graphics. This format is popular when we want to include transparent areas in our image. In this case, the transparent area would be the background.
Just so we can see the difference. Click the image format selector again and choose jpg, Joint Photographic Experts Group. This format does not support transparency. This is why we see the white canvas area around the image. Return to the PNG format.
Click the download button. The image is downloaded immediately. Click the “X” button to close the export options.
Click the page above the image we just exported. Repeat the process to export this image. Make sure the image format is set to PNG and click the download button. Repeat the process for the rest of the pages and images. Each image file is named Dice Face Image followed by a number. Except for the first image. You can rename the images or upload them to your Scratch project with this name. I recommend renaming the images.
Trigger mBot code with event inputs
In this article, we pick up where we left of last week. You will learn how to use inputs from the mBot remote to control when the robot runs code. You will learn how to use the button on the robot to do the same operation. In the end, we will combine them into one code block.
Using the remote
In last week’s article, mBot Robot and Basic Motion, we used a simple code block to move our robot forward. This allowed us to use the robot to learn about motion, velocity, and acceleration. By adjusting the power applied to the motors we increased or decreased the velocity. The robot travels longer or shorter distances when we adjust the duration that power is applied to the motors.
I’m sure you adjusted the code and uploaded it several times. Each time you had to take care that the robot didn’t run off the desk or table. I’m sure this proved inconvenient on more than one occasion.
We are going to place a condition in our code so the robot doesn’t begin to move as soon as we upload our code. A condition is an event that must take place before segments of code are performed.
The robot comes with a remote. It doesn’t come with a battery though. You will need to insert one. I believe it is a CRC-2032 battery. This remote will serve as our event.
Open the mBlock software and create a new project. Title the project Remote Event. Load the mBot code library. Click the Add button in the devices panel.
Click on the mBot icon and click the Add button to load the libraries.
Go to the Control category. Find the Forever code block. This is a loop that will repeat the steps we place inside. It will repeat these steps until we turn the robot OFF.
Place the Forever block on the canvas.
Drag the “If…then” code block and place it within the Forever loop.
Go to the Actions category. Find the move forward code block. Place the block inside the “If…then” condition.
We need to set the condition to begin the Move code. Go to the Sensor category.
Look for the “IR remote A pressed?” code block.
Place the code block inside the condition parameter. The parameter will highlight when the piece is in the right position.
The remote code block has a parameter. This parameter waits for one of the buttons on the remote to be pressed. The “A” button is automatically selected. Click the triangle next to the letter to reveal more button options.
Select the “Up” button. I recommend each student uses a different button. This will prevent the robot from receiving a signal from a stray remote.
The code is complete. Upload the code to the robot. The robot will not move as soon as the program is uploaded. Disconnect the robot and place it on a flat surface. Press the Up button on the remote. The robot will move forward for 3 seconds. Press the Up button again and the robot will move forward again for 3 seconds.
The robot repeats the process because we placed the condition inside a forever loop. The condition does not need to be placed within the Forever loop. Placing the condition in the loop makes it convenient if we want to run the code blocks again and again. Without the Forever loop we would need to turn the robot OFF then On again to use the remote to trigger the event.
Use this code block for any future projects. Place all your code within the condition block.
Using the onboard button
You might not have a remote with the robot or a battery for the remote. There is a button on the robot we will use to trigger the event. The code for the onboard button is almost identical. Click and drag the IR remote code block out of the If…then parameter.
Drag the IR remote code over the Code panel. The panel will change to a light grey color. A trashcan will appear. Release the code block.
Look for the “When on-board button pressed” code block. It is in the Sensor category.
Place the code block in the parameter for the condition block. The code block has a parameter. The parameter is set to the button pressed. This is what we want.
The code is all set. Upload this to the robot. Press the button on the mBot. Using a button is a good option if you don’t want a remote from another robot to trigger the event on your robot.
Combine conditions
The IR remote and button can both be used. We will place both conditions in one code block. To use both conditions we need to use an operator. We are going to use a Boolean operator. There are three Boolean operators. They are AND, OR, and NOT. They are often used to connect and define relationships.
Remove the “When on-board button pressed” code and leave it on the canvas.
Go to the Operators category. Find the “or” operator.
Place the OR operator in the "If…Then" condition parameter. The OR operator has two parameters. The code for the button will be on one side. The code for the IR remote will be on the other. One condition or the other must be met for the move action to take place.
Place the “when on-board button pressed” code on the right side of the OR operator. It doesn’t make a difference on which side it is placed. The OR operator will work the same.
Find the IR remote code in the Sensor category. Place it on the left side of the OR operator. Choose a button to trigger the event.
Upload the program to the robot. Try the remote or the button. One of them will start the robot moving.